Introduction
引言
Science and technology (S&T) competition has increasingly become an important part of the strategic competition among powers. The technological progress of emerging countries will affect the distribution of power in international relations, and their innovative activities may have externalities on dominant countries. Therefore, when any country makes a breakthrough in S&T competition, this will help the country gain an advantage in the fierce competition among nations. As a representative of cutting-edge technologies in recent years, the impact of the development trend of artificial intelligence (AI) on the international community has gradually become apparent: Both the series of S&T wars launched by the United States against China and the technological alliances established by the United States, Japan, South Korea, and other countries to restrict China’s S&T development exhibit the characteristics of scientific and technological competition. In particular, the emergence of the sensational application ChatGPT at the end of 2022 once again highlighted the urgency of S&T competition. As a generative AI launched by OpenAI, ChatGPT features “strong interaction,” “strong understanding,” and “strong generation.” Through dialogue with ChatGPT, people can quickly retrieve information, write abstracts of papers, write computer applications, and perform other operations. Compared with the AI of the past, these breakthrough capabilities have allowed people to see the dawn of the development of artificial general intelligence. This type of AI is an AI system with universal applicability, autonomy, creativity, and learning capabilities. This is expected to become an important driving force for the progress of human society. Microsoft Chairman and CEO Satya Nadella excitedly stated that ChatGPT will be a killer application that changes productivity and the way we work in the future. From the perspective of national security governance, the application of AI in the cognitive and physical domains can certainly improve the country’s governance level in the security field. However, the rapid development of AI based on big data models as represented by ChatGPT has significantly expanded the breadth and depth of the content and fields involved in the national security field in a short period of time. The widespread use of this type of AI will profoundly change the security situation countries face.
科技竞争愈发成为大国战略竞争中的重要一环。新兴国家的技术进步会影响国际关系中的权力分配,其创新活动可能会对主导国家产生外部性影响,因而任何国家在科技竞争中的突破都将有助于该国在激烈的国家竞争中占得优势。人工智能作为近年来前沿科技的代表之一,其发展态势对国际社会的影响逐渐凸显:无论是美国对中国开展的一系列科技战,还是美日韩等国围绕限制中国科技发展而建立的技术同盟,都展现出科学技术竞赛的特征。特别是2022年年底现象级应用ChatGPT的出现,再次彰显出科技竞争的紧迫性。作为由OpenAI公司推出的生成式人工智能(Generative AI),ChatGPT具备“强交互”“强理解”“强生成”等特点,人们可以通过与ChatGPT对话进行快速检索信息、撰写论文摘要和编写计算机应用程序等多种操作。这些相较过往人工智能出现的突破性能力,让人们看到了研发通用型人工智能(Artificial General Intelligence)的曙光。该类人工智能是具有普适性、自主性、创造性和学习能力的人工智能系统,有望成为推动人类社会进步的重要驱动力。微软董事长兼首席执行官萨蒂亚·纳德拉(Satya Nadella)惊叹,ChatGPT将是未来改变生产力和工作方式的杀手级应用。从国家安全治理来看,人工智能在认知域和物理域的应用的确能提升国家在安全领域的治理水平,但以ChatGPT为代表的基于大数据模型下快速发展的人工智能,短时间内大幅扩展了其在国家安全领域涉及内容和领域的宽度和深度,对此类人工智能的广泛使用将深度改变国家面临的安全态势。
In recent years, discussions on the development of AI and international relations both inside and outside China have increased, and specific issues of concern have gradually turned to international political and national security issues, such as the relationship between AI technology and national power. In current research, scholars’ discussions of political issues around AI as represented by ChatGPT mainly include the following: The first is the relationship between the development of AI technology and changes in power among countries. As AI becomes the core force behind a new round of industrial revolution and is seen as the “technical foundation” of the innovation paradigm of the future, AI research has become a key factor for countries vying for S&T supremacy. Therefore, the current contest among technological powers in AI research will lead to increasingly fierce competition among countries. The changing composition of national power will further disrupt the originally stable structure of the balance of power. The strategic behavior of countries will change, and the gap between developed countries and developing countries will gradually widen. The second is the increasing complexity of AI and the national security situation. Some studies argue that the widespread use of AI will make the security situation that countries face more complex. The application of AI in military equipment has partially changed the format of war, and the United States and Western countries have become more willing to launch regional wars. The third is research on the impact of ChatGPT itself. At present, the focus of academic circles is on the impact of the emergence of ChatGPT on academic ethics and social development, with less attention paid to the impact of ChatGPT on the current national security situation.
近年来,国内外有关人工智能与国际关系发展的讨论逐渐增多,关注的具体议题逐步转向人工智能技术与国家权力之间关系等国际政治和国家安全方面的议题。从当前研究看,学者们围绕以ChatGPT为代表的人工智能开展政治类议题讨论主要包括以下几种:一是人工智能技术发展与国家间权力变化间的关系。随着人工智能成为新一轮产业革命的核心力量,其被认为是未来创新范式的“技术基底”,人工智能研究成为各国争夺科技竞争权的抓手之一。因此,当前技术大国在人工智能研究方面的较量会导致国家间竞争态势愈发激烈,国家权力的组成发生变化并进一步打破原本稳定的权力均势结构,国家的战略行为发生改变,发达国家与发展中国家之间的差距将会逐步放大。二是人工智能与国家安全态势复杂化。部分研究认为,对人工智能的广泛运用会使国家面临的安全态势更加复杂, 人工智能在军事装备上的应用部分改变了战争形态,美西方国家发动地区性战争的意愿更加强烈。三是研究ChatGPT本身带来的影响。目前,学界关注重点在ChatGPT的出现对学术伦理带来的冲击与对社会发展的影响上,但是较少涉及ChatGPT对当前国家安全形势的影响。
The research discussed above makes a relatively comprehensive study of the relationship between AI and the development of international relations from the perspectives of changes in power, the transformation of the international power structure, and competition between major powers. However, current research focuses on the relationship between AI and the relative dynamics of power among countries. There is relatively little research on the impact of the development of generative AI as represented by ChatGPT on national security. With the progress of the times and the advancement of technology, the intrinsic meaning of security and power are changing. In the field of non-traditional security, power is present at the traditional technical level and in the game of international systems and standards, and is also reflected at the level of discourse in the struggle for dominance. Power manifests itself in technical power, institutional power, and discursive power. Although discursive power is less obvious than the other two types of power, in a sense, it is only when a country’s comprehensive power in multiple dimensions is enhanced that this country can safeguard its rights and interests in this field. Different from any previous technological progress, ChatGPT’s discursive power is shaped by technology and manifested in human-computer interaction. This means that whoever can influence the input content and output preferences of the machine by setting its algorithms will hold discursive power. Compared with all previous strategic power games, the ideological penetration and security risks caused by this game are more subtle. The setting of algorithms and content preferences will be decisive factors in the production of discursive power. The emergence and development of generative AI as represented by ChatGPT will further increase the intensity of the discursive power game among countries and will also further enrich and rewrite the meaning of security.
上述研究主要从权力更迭、国际权力结构转变和大国竞争等角度,对于人工智能和国际关系发展之间的关系进行了比较全面的研究。但是当前研究聚焦于国家间权力相对发展与人工智能之间的关系,对以ChatGPT为代表的生成式人工智能发展对国家安全态势的影响研究相对较少。随着时代的发展和技术的进步,安全的内涵和权力的内涵都在发生变动,在非传统安全领域,权力体现在传统的技术层面以及国际制度和标准的博弈上,同时也反映在话语层面的主导权争夺上,其表现为技术性权力、制度性权力和话语性权力。尽管话语性权力相较其他两种权力不那么瞩目,但在某种意义上,只有国家在多个维度上的综合性权力提高了,国家在该领域内的权益才能得到保障。与以往任何一种技术进步不同的是,ChatGPT的话语权塑造依托于技术,表现为人机交互。即谁能通过设定算法,影响机器的内容输入和输出偏好,谁就掌握了话语性权力。相比以往任何一种权力博弈,这种博弈所造成的意识形态渗透和安全风险都更为隐性。对算法的设定和对内容偏好的设定将是生产话语性权力的决定性因素。以ChatGPT为代表的生成式人工智能的出现与发展,将进一步提高国家在话语性权力方面的博弈强度,亦将重新丰富和书写安全的内涵。
Every technological revolution in history has brought immense changes to the economy and society, but they have also brought new challenges and imposed new requirements for national governance systems and governance capabilities. From the perspective of maintaining national power and national security, we must squarely face the challenges and opportunities brought by this technology. Therefore, this article aims to answer the following questions: In the context of increasingly fierce competition among countries for dominance in the AI field, how are ChatGPT and generative artificial intelligence different from the AI of the past? How will this type of AI change the features of the current state of national security? What methods should we adopt to respond to changes in real security challenges? The answers to the above questions will help us squarely face the challenges that the new technologies are bringing to national security and provide a reference for maintaining the national security order and taking hold of the development of the security situation.
历史上每次技术革命在给经济社会带来巨大变化的同时,也给国家治理体系和治理能力带来新的挑战,提出新的要求。从维持国家权力与国家安全的角度出发,我们必须正视该技术带来的挑战与机遇。因此本文旨在解答以下问题:在各国有关人工智能领域主导权竞争愈发激烈的大背景下,ChatGPT和生成式人工智能与以往的人工智能有何不同?此类人工智能会对现有国家安全的特征带来什么改变?我们应通过什么方式应对现实安全挑战的变化?对以上问题的回答有助于我们正视新技术对国家安全带来的挑战,为维护国家安全秩序、把握安全局势发展提供参考。
I. The development of AI technology and the rise of ChatGPT
一人工智能技术发展与ChatGPT崛起
ChatGPT and related technologies are the latest data points plotting out the rapid development of AI technology. To understand the impact of ChatGPT on current societal development and international security, we must first understand the operating mechanisms of ChatGPT and how it changes and impacts the combined application of AI technology.
ChatGPT及相关技术是人工智能快速发展技术路径上的最新数据点。要理解ChatGPT对当前社会发展和国际安全态势的影响,首先要理解ChatGPT的运行机理及其对人工智能技术组合应用带来的变革及影响。
(i) The development of AI technology and the features of ChatGPT’s capabilities
(一)人工智能技术发展与ChatGPT的能力特征
Research on AI began in 1956 when scientists such as John McCarthy and Marvin Lee Minsky discussed how to use machines to simulate human intelligence. The concept of “artificial intelligence” proposed in these discussions opened the door to research in the academic discipline of AI. After several technological upgrades, breakthroughs were continuously achieved in the technological development and application of AI. The nature of the technology AI is based on has gradually shifted from the “logical reasoning” of the 1.0 era to the “knowledge engineering” of the 2.0 era and then to the “machine learning” of the 3.0 era. Along the way, AI capabilities improved rapidly, and the scope of applications gradually expanded. After the third wave of AI technology development, AI technology has also crossed the threshold of industrialization, gradually taking on the characteristics of a systemic variable in the international system. Countries continue to expand the scope and depth of their applications of AI technology in military, economic, and other fields: Smart weapons and information processing platforms such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have gradually changed the face of traditional warfare, and AI’s empowerment of industries and innovation have greatly increased the rate of production and economic development. AI is seen as an important part of the new round of S&T revolution. As early as 2016, analysts realized that the development of AI technology has crossed the threshold of affecting human political life and would become an important influencing factor in the international system in the future. The unprecedented importance of AI technology and equipment may make policies for this field into the most critical element of national policy. The United States is well aware of the significant momentum that AI contains in the fields of national defense, military affairs, and industrial innovation. Therefore, it has always closely linked leadership in AI with the maintenance of U.S. hegemony, continuously introducing many AI development strategies. The competition for the initiative in AI technology R&D and application has become an important component part of the S&T competition between major powers.
有关人工智能的研究起源于1956年约翰·麦卡锡(John McCarthy)和马文·明斯基(Marvin Lee Minsky)等科学家对有关如何用机器模拟人的智能的探讨。探讨中提出的“人工智能”(Artificial Intelligence)概念,打开了人工智能学科研究的大门。在历经数次技术升级后,人工智能的技术发展与应用不断取得突破,其所依据的技术本质从1.0时代的“逻辑推理”,逐步转向2.0时代的“知识工程”与3.0时代的“机器学习”,人工智能能力快速提高,适用范围逐步扩大。在人工智能技术发展的第三次浪潮后,人工智能技术也跨越了产业化的门槛,逐步呈现出国际体系中系统性变量的特征。国家不断扩大人工智能技术在军事、经济等领域的应用范围与深度:无人机等智能武器与信息处理平台逐步改变了传统战争的面貌,人工智能对产业的赋能与革新大幅提高了生产与经济发展速率,被认为是新一轮科技革命的重要组成部分。早在2016年,已有分析者意识到人工智能技术的发展已经跨越了影响人类政治生活的门槛,未来将成为国际体系中的重要影响因素,人工智能技术和设备史无前例的重要性可能使该领域的政策成为国家政策中最关键的要素。美国深知人工智能在国防军事、产业革新等方面蕴含的重大动能,因而始终将领跑人工智能与护持美国霸权紧密联结,不断出台多项人工智能发展战略。人工智能技术的研发和应用主动权竞争成为大国科技竞争的重要组成部分。
S&T companies also continue to accelerate the pace of their exploration of AI technology development. In 2017, Google proposed a new AI deep learning model, the Transformer model. The researchers introduced a self-attention mechanism into the model and proposed a multi-head attention mechanism that can improve the parallel efficiency and operational performance of the model, greatly improving the computational speed of AI when faced with large-scale data. This gives AI strong abilities to understand contextual relationships. After that, OpenAI developed the Generative Pre-Training (GPT) model based on the Transformer model, introducing an unsupervised pre-training mechanism and supervised fine-tuning method into model training. This, combined with the prompt learning method, gives AI powerful natural language understanding capabilities. OpenAI successively developed several versions based on the GPT model. By the time it reached the GPT-3 model, the number of parameters used to train the model had reached 175 billion, achieving in-context learning and allowing the model to produce high-quality answers from a small number of samples. ChatGPT is a conversational AI launched by OpenAI based on the GPT-3.5 model. Researchers at OpenAI introduced the reinforcement learning from human feedback method into the training of ChatGPT. Engineers provided dialog data during AI training, created and used the reinforcement learning reward model, and used proximal policy optimization to fine-tune the model. AI sorts the generated answers by ranking method during the training and learning process, and feeds them back to the system for a new round of training. This way, it can learn the expressions and grammatical rules of human language through large-volume training, thereby simulating the generation process of human language. Therefore, ChatGPT can generate text content in a more natural manner and is viewed as a new-generation knowledge invocation and processing tool. The combination of the above technologies gives ChatGPT more unique capabilities compared to traditional AI.
科技公司也在继续加快探索人工智能技术发展路径的脚步。2017年,谷歌公司提出新的人工智能深度学习模型Transformer模型。研究人员把自注意力(Self-Attention)机制引入模型内部,提出能够提高模型并行效率和运行效果的多头注意力机制(Multi-head Attention),大幅度提高人工智能在面对大规模数据时的运算速率,使其具有良好的理解上下文关系的能力。此后,OpenAI公司基于Transformer模型开发出GPT(Generative Pre-Training)模型,将无监督预训练机制和有监督微调方式引入对模型的训练中,结合提示学习(Promote Learning)方式,使得人工智能具备了强大的自然语言理解能力。OpenAI公司基于GPT模型陆续开发数个版本。到GPT-3模型时,用以训练模型的参数规模已达1 750亿,实现了情景学习(In-context Learning),使得该模型可以通过少量的样本便产生高质量答案。ChatGPT便是OpenAI公司基于GPT-3.5模型推出的对话型人工智能。OpenAI公司的研究人员将基于人类反馈的强化学习方法(Reinforcement learning from human feedback)引入对ChatGPT的训练,由工程师在训练人工智能时提供对话数据,创建和使用强化学习的奖励模型(Reward Model),使用最近策略优化(Proximal Policy Optimization)来微调模型。人工智能则在训练学习过程中将生成的答案通过排名方式排序,并反馈到系统中开展新一轮训练,使其能够通过大量训练习得人类语言的表达方式和语法规则,从而能够模拟人类语言的生成过程。因此,ChatGPT可以较为自然地生成文本内容,被视为是新一代知识调用和处理工具。以上这些技术的组合,共同赋予了ChatGPT相较于传统人工智能更独特的能力。
Figure 1 Features of ChatGPT
图1 ChatGPT特点
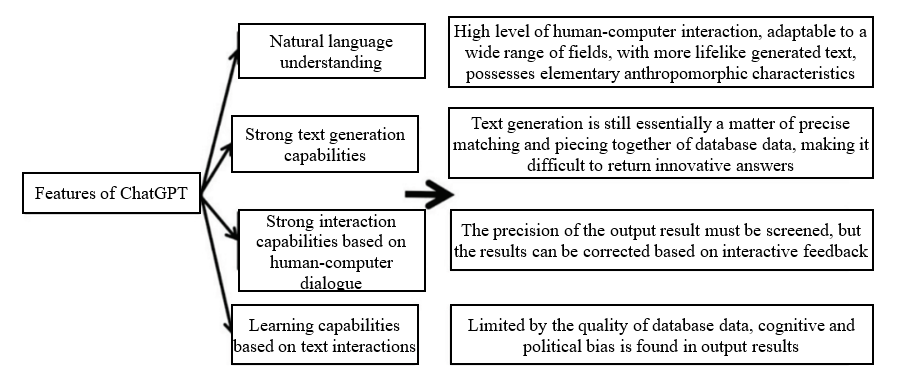


First, in terms of linguistic expression, ChatGPT can efficiently understand and interpret human language and produce corresponding answers that conform to the laws of natural language, demonstrating strong anthropomorphic expression capabilities. Based on reports, ChatGPT is capable of generating impressive, detailed, human-like written text. Compared with the mechanized and programmed expressions found in interactions with previous AI systems, the ChatGPT model has a built-in scientific and humanized AI language system. Its surprising language “understanding” and expression capabilities exceed those of 90% of people. This enables ChatGPT to rid itself of the lack of emotional expressions found in the output process of previous AI systems during its operation. ChatGPT can conduct basic logical deductions and emotional judgments based on the conversation content, and output text that is as consistent with the context and language characteristics as possible. This gives it broad prospects for use in human-computer interaction fields such as text translation.
第一,在语言表达方面,ChatGPT能够高效理解和解读人类语言,并相应地产出符合自然语言规律的回答,展现出极强的拟人化表达能力。据报道,ChatGPT能够生成令人印象深刻的、详细的、类似人类的书面文本。相较于以往人工智能在交互过程中的机械化、程序化表达,ChatGPT模型内置了科学化和人性化的人工智能语言系统,其出人意料的语言“理解”和表达能力,已经超过90%的人, 使得ChatGPT在运行过程中能够摆脱以往人工智能输出过程中缺少感情色彩的表达方式,并能根据对话内容进行基本的逻辑推演和情感色彩的判断,输出尽可能符合语境和语言特点的文本。这使得其在文本翻译等人机交互领域表现出广阔的使用前景。
Second, ChatGPT shows far superior capabilities compared to traditional AI. ChatGPT shows people the capabilities and potential of large language models based on deep learning, that is, large-scale models with parameters in the hundreds of billions, which can break the traditional scaling law to achieve a qualitative leap in model capabilities. ChatGPT has already demonstrated document translation, data code writing, and other capabilities. The latest GPT-4 model has further demonstrated advanced reasoning capabilities that far exceed ChatGPT, and can even produce functional websites based on handwritten requirements in a few minutes. These capabilities make ChatGPT an auxiliary tool that can greatly improve the efficiency of learning and research. At the same time, ChatGPT also possesses strong learning capabilities. The AI of the past rarely had the ability to make interactive corrections, and its answers were often based on certain “patterns” that were “summarized” from the data. Once the information received did not conform to these patterns, the answers it gave would deviate significantly. Based on self-reinforcement learning through unsupervised pre-training and human feedback, ChatGPT can continuously correct errors in interaction with human discourse and autonomously strengthen its language processing capabilities. Limited by the size of the training database and the failure to update the training data in a timely manner, ChatGPT sometimes makes minor or even common-sense errors. However, it quickly makes corrections and produces records after receiving user feedback. After multiple rounds of training, the accuracy of its output results significantly improves, and it achieves a high degree of intelligentization through continuous technological iteration. Of course, limited by its training data and algorithms, ChatGPT may sometimes “talk nonsense in a very serious tone.” This requires a further strengthening of algorithm capabilities and expansion of the scale of data used in AI training to improve the accuracy and precision of its answers.
第二,ChatGPT相较传统人工智能而言展现出超强的能力。ChatGPT向人们展现出基于深度学习的大语言模型的能力与潜力,即参数达到千亿级别的大规模模型,这能够打破传统的比例定律进而实现模型能力质的飞跃。ChatGPT目前已展示出文档翻译、数据代码编写等能力,最新的GPT-4模型更是展现出远超ChatGPT的高级推理能力,甚至可以在几分钟内基于手写需求产出功能性网站。这些能力使得ChatGPT作为辅助工具,可以大大提高学习与研究效率。同时,ChatGPT还具有极强的学习能力。以往人工智能较少拥有交互修正能力,其回答往往是依据数据“总结”出的某些“规律”,一旦接收到的信息不符合该规律,那其作出的回答就具有较大偏差。ChatGPT通过无监督预训练和人类反馈的自我强化学习,可以在与人类的话语互动中不断纠错,自主强化语言处理能力。尽管受限于训练资料库规模、训练资料未能及时更新等原因,ChatGPT有时会出现低级甚至是常识性错误,但其在接收到用户反馈后会及时进行修正并记录,在多次训练后显著提高输出结果的准确率,通过不断技术迭代,实现高智能化。当然,受限于训练数据及算法,ChatGPT有可能出现“一本正经地胡说八道”的情况。这就需要进一步强化算法能力与扩大人工智能训练的数据规模,以提高回答的准度与精度。
Third, the emergence of ChatGPT has made people realize the broad application prospects of generative AI. As a generative AI, ChatGPT can improve natural language processing and natural language understanding in many applications, and demonstrates the ability to generate multi-modal information. In addition to language-based question and answer, ChatGPT has shown us a variety of functions including language translation and text summarization and generation. This reflects the outstanding advantages of generative AI, namely, the ability to generate new content based on training data rather than simply logically arrange knowledge. The AI developed in the past was mainly decision-making AI, which primarily learns the conditional probability distribution in the data and then performs analysis and makes judgments based on the data. Starting from this basis, generative AI has achieved a breakthrough. It can not only perform prediction functions similar to decision-making AI, but can also perform in-depth learning, induction, and creation based on large amounts of data. After receiving instructions, it can independently make judgments and generate corresponding content. Currently, generative AI is being used in many fields, including ultra-high-definition video generation, remote medical diagnosis, and computer code generation. People with no basic skills in painting can even use AI to create award-winning paintings. Generative AI is likely to be the main direction of future AI development. It is foreseeable that, as the training cost of generative artificial intelligence decreases and computing efficiency improves, more auxiliary tools will be used in fields such as drug and chip design. Researchers can optimize product design layouts with the assistance of such AI, reducing the cost and time required for drug and material discovery, and thus greatly improving industry productivity.
第三,ChatGPT的出现使得人们认识到生成式人工智能所具有的广阔应用前景。ChatGPT作为生成式人工智能,能够在许多应用中改善自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing)和自然语言理解能力(Natural Language Understanding),展现出多模态信息的生成能力。除语言问答外,ChatGPT已经为我们展示了包括语言翻译、文本摘要与生成在内的多种功能,这反映出生成式人工智能的突出优势,即能够基于训练数据生成新的内容而非对知识进行基本的逻辑排列。以往开发的人工智能主要是决策式人工智能,主要学习数据中的条件概率分布,根据数据进行分析判断。生成式人工智能则在此基础上实现突破,不仅能够与决策式人工智能发挥类似的预测功能,还能够基于大量数据进行深度学习、归纳及创造,在接收指令后能独立作出判断与生成对应内容。目前,生成式人工智能已被运用在包括超高清视频生成、远程医疗诊断、计算机代码生成等在内的多个领域,没有绘画基础的人甚至能借助人工智能创作绘画作品并获奖。生成式人工智能很可能将是未来人工智能的主要发展方向。可预见的是,随着生成式人工智能的训练成本下降和计算效率的提高,会有更多辅助性工具被用在药物和芯片设计等领域,研究人员可以通过此类人工智能的辅助优化产品设计布局,降低药物和材料发现的成本与时间消耗,以此大幅提升行业生产效率。
(ii) ChatGPT intensifies competition among S&T companies and pushes society to consider it from all sides
(二)ChatGPT激化科技企业竞争态势 引发社会多方位思考
The emergence and popularity of ChatGPT have attracted S&T giants to continue to increase their investment in AI research, launching a new round of competition in this field. In terms of the development of AI technology, after OpenAI launched ChatGPT based on the GPT-3.5 model, it continued on to launch the GPT-4 model that provides stronger comprehensive capabilities. Google has accelerated the training of ChatGPT-like AI and launched the latest version of the large language model PaLM and a new tool MakerSuite. Developers can use this tool to rapidly prototype their own ideas, achieve real-time engineering, generate synthetic data, adjust custom models, and perform other functions. Chinese S&T companies and universities are also stepping up their efforts to develop ChatGPT-like AI in an attempt to catch up with this wave. For example, Baidu quickly launched a large model “Wenxin Yiyan,” benchmarked against ChatGPT.
ChatGPT的出现与火爆吸引了科技巨头继续加大对人工智能研究的投入,在该领域展开新一轮竞赛。在人工智能技术发展方面,OpenAI公司在推出基于GPT-3.5模型的ChatGPT后,继续推出综合实力更加强大的GPT-4模型。谷歌公司加速对类ChatGPT人工智能的训练,并推出大语言模型PaLM的最新版本和新工具MakerSuite,开发人员可以通过该工具对自身想法进行快速原型设计,实现即时工程、生成合成数据和调整自定义模型等功能。国内科技企业与高校也加紧步伐开发类ChatGPT人工智能,试图赶上这波浪潮。例如,百度公司迅速推出大模型“文心一言”对标ChatGPT等。
At the same time, ChatGPT’s powerful capabilities have impacted many areas of society. ChatGPT is essentially a conversational AI, and its output results are mainly text. Therefore, in some information exchange fields based on text exchange, ChatGPT will have a transformative impact on existing interaction and production methods. In the field of education, for example, ChatGPT’s multi-modal applications, information retrieval, and result production capabilities will gradually revolutionize the existing education system. It will not only serve as a “prosthetic limb” to gradually narrow the gap between the knowledge-disadvantaged and others, but also improve the ease of use and accuracy of the adaptive learning systems and enhance the completeness and creativity of teaching results. In the field of public administration, ChatGPT’s rapid processing capabilities for text and other data enable it to help the national government quickly handle certain public matters and realize the integrated development of intelligent government affairs including intelligent decision-making, intelligent management, intelligent services, and intelligent supervision. However, social changes are often accompanied by corresponding risks. As a new knowledge invocation tool, ChatGPT brings ethical risks and knowledge plagiarism to the academic world, which also makes whether to allow its use in academic research a controversial issue. Some people believe that “ChatGPT may be the end of civilization.” They think that widespread reliance on ChatGPT will make people lose their critical thinking. Therefore, how to define the role of similar AI in papers and experiments has become a major problem that the academic community will face.
同时,ChatGPT拥有的超强能力给社会多个领域带来冲击。ChatGPT本质上是一个对话式人工智能,其产出结果方式主要是文本输出,因而对于某些基于文本交换进行信息交流的领域,ChatGPT将会对既有的互动与生产方式产生变革性冲击。例如,在教育领域,ChatGPT拥有的多模态应用、信息检索与结果产出能力将逐步变革现有教育体系,不仅作为“义肢”逐步缩小知识弱势者与他人的差距,还能够提高自适应学习系统的易用度与准确度,提升教学成果的完成度与创意感。而在公共管理领域,ChatGPT拥有的对文本等数据的快速处理能力使其能够帮助国家政府快速处理部分公共事项,并实现包含智能决策、智能管理、智能服务和智能监管在内的智能政务一体化发展。 但是,社会变革往往也伴随着相应风险。ChatGPT作为新型知识调用工具,其给学术界带来的伦理风险、知识剽窃行为也让人们在允许其介入学术研究这一问题上存在争议,有观点认为,“ChatGPT可能是文明的终结”,认为对ChatGPT的广泛依赖将会让人的思维失去批判性。因而如何界定类似人工智能在论文和实验中的角色,成为学术界将要面临的一大难题。
The potential security risks brought about by ChatGPT have caused widespread concern in society. Elon Musk believes that AI (as represented by ChatGPT) is “both positive or negative and has great, great promise, great capability,” but that “with that comes great danger.” Viewed from the level of national security, the impact of the development of ChatGPT and AI on national security has received widespread attention. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology released an AI risk management framework to help researchers think about the development of AI technology, and measure and monitor AI risks and their potential negative impacts. Italy has banned the use of ChatGPT on the grounds of leakages affecting “personal privacy.” At the societal level, the shock caused by ChatGPT also made people worry about the breakthrough development of AI. In Japan, nearly 70% of respondents believe that the country should impose stricter supervision on the development of AI. From this, we can see that ChatGPT will not only have impactful results on traditional AI application fields, but its unpredictable functions and application spillovers will also have a multi-faceted impact on society. Therefore, discussing the impact of the emerging applications of ChatGPT on national security will not only help to clarify doubts about its application and the technical mechanism behind this, but also help to comprehensively understand and correctly view the disruptive influence of generative AI on society in the future.
ChatGPT可能带来的安全风险引发社会的广泛担忧。埃隆·马斯克(Elon Musk)认为,“(以ChatGPT为代表的)人工智能具有巨大的前景与强大的能力,但随之而来的也是巨大的危险”。从国家安全层面看,ChatGPT和人工智能发展对国家安全带来的影响已被广泛关注。美国国家标准与技术研究院发布人工智能风险管理框架,旨在帮助研究者思考人工智能技术发展、衡量和监控人工智能风险及其潜在消极影响。意大利则曾以“个人隐私”泄露为由禁止ChatGPT在意大利境内的使用。 在社会层面,ChatGPT带来的震撼也使得人们对人工智能的突破性发展感到担忧。在日本,接近70%的受访者认为,国家应该对人工智能的发展进行更加严格的监管。由此可见,ChatGPT并不只对传统人工智能应用领域带来冲击性结果,其难以预料的功能和应用外溢也将给社会带来多方位影响。因此,围绕ChatGPT这项新兴应用对国家安全带来的影响展开讨论,不仅有助于对该项应用及背后技术机理的释疑,更有助于全面理解和正确看待生成式人工智能对未来社会的颠覆性影响。
II. New features of national security under the influence of ChatGPT
二 ChatGPT影响下的国家安全新特征
High-tech innovations and breakthroughs have had multiple overlapping influences on national development. From the perspective of international power comparisons, a new round of scientific and technological revolution carried by AI technology is accelerating the reshaping of the global power order. From the perspective of social and economic development, AI can help countries establish a more sustainable growth model that is free from economic crises. Looking back at the development and evolution of several technological revolutions from the past, we can see that they often have a significant or even disruptive impact on national security. The “cross-field extensibility” of national security studies naturally coincides with the broad adaptability of AI, and the development of AI technology is naturally deeply embedded in various national security fields. In the fields of political security, economic security, and military security, AI, as a systemic element itself, will create a wide range of new issues and become the central node of an issue network. In the fields of network security, nuclear security, and homeland security, where security has a relatively specific meaning, AI will become an important enabler, shaping the semi-central area of the network. The remaining national security fields are more loosely linked to AI, forming the peripheral area of the issue network. Therefore, it is very important to explore the multiple overlapping influences of ChatGPT on the national security situation.
高新技术的革新与突破给国家发展带来多重影响。从国际权力对比看,以人工智能技术为载体的新一轮科学技术革命正在加速重塑世界权力秩序。从社会经济发展的角度看,人工智能可以帮助国家建立更加可持续的、免于经济危机侵扰的增长模型。回顾过去数次技术革命的发展与演变,其往往会对国家安全态势产生重大甚至是颠覆性影响,国家安全学的“横切延伸性”特征与人工智能的广泛适应性特点天然契合,人工智能技术发展自然深度嵌入到国家安全各领域。在政治安全、经济安全和军事安全领域,人工智能将以系统性要素的身份创建广泛的新议题,并成为网络的中心节点;在安全内涵相对具体的网络安全、核安全与国土安全领域,人工智能则成为重要的赋能主体,塑造了网络的半中心区域。其余国家安全领域与人工智能的链接相对松散,构成议题网络的外围区域。因此,探究ChatGPT对国家安全态势带来的多重影响非常重要。
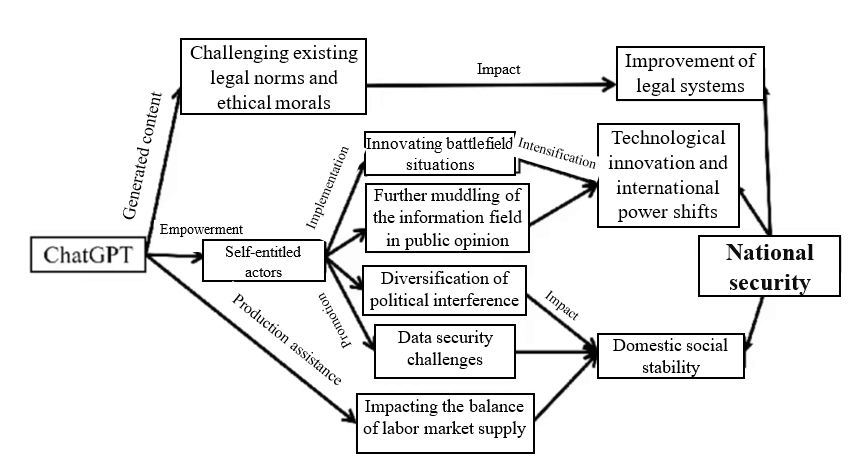
(i) The information field will become more complex, increasing the ability of some countries to manipulate international public opinion
(一)信息场域进一步复杂化 助长部分国家操纵国际舆论的能力
Developed Western countries are relatively mature in the AI field, so they have been able to strengthen their control over international public opinion by seizing opportunities and technological advantages. This is more conducive to their values-based targeted manipulation of public opinion and the establishment of information cocoons. Rapidly developing AI will facilitate the generation of disinformation, allowing the creation of a false appearance of consensus and hiding underlying societal fractures. For a long time, the United States has relied on its S&T hegemony and international voice established after World War II. Through its control of international media, the United States has continued to project anti-China public opinion and a negative image of China with views such as the “debt threat theory” and “economic aggression theory.” In terms of propaganda strategies, the Western media often only take up political issues and human rights issues that are in line with Western interests in order to set the agenda, while focusing on negative issues in their reporting. Once this sort of public opinion gains dominance, it can hide its value orientation under the cloak of “collective will” through discourse suppression and creation functions. Generative artificial intelligence, as represented by ChatGPT, has great advantages in conducting public opinion wars: After purposeful training, this type of AI can continuously output speech that is politically biased and contains false information, and convert such speech into the formats of images, videos, and online speech. When exported to international data networks through various public opinion communication channels, this speech will directly or indirectly interfere with international public opinion and affect the public perception of other countries. On this basis, countries with technological and data advantages can combine AI developed based on big data models with various Internet bots to create a new type of “cyber army.” By mixing in false information and distorting facts, this army can concoct large volumes of speech that smear the images of other countries. This not only directly affects public opinion and tarnishes the images of other countries, but also helps the perpetrating countries strengthen their dominance and initiative in the field of international public opinion.
西方发达国家在人工智能领域发展较为成熟,得以通过抢占先机和技术优势强化对国际舆论的掌控能力,更有利于它们基于价值为导向有针对性地操控舆论,建立信息茧房。快速发展的人工智能将会助长虚假信息的产生,制造虚假的共识表象并隐藏潜在的社会裂痕。长期以来,美国凭借二战后确立的科技霸权与国际话语权,通过对国际传播媒体的控制,持续输出反华舆论,以“债务威胁论”“经济侵略论”等观点输出中国的负面形象。在宣传策略上,西方媒体往往仅是截取符合西方利益诉求的政治议题、人权议题进行议程设置,对负面议题进行集中报道。一旦这种舆论获得主导地位,它就能通过话语的压制和创造功能为其价值取向披上“集体意志”的外衣。而以ChatGPT为代表的生成式人工智能在进行舆论战时具备极大优势:此类人工智能在进行有目的性的训练后能够持续不断地输出带有政治偏见与虚假信息的言论,并将其以图片、视频和网络言论等形式,通过各种舆论传播渠道输出到国际数据网络中,直接或间接干扰国际舆论,并且影响他国民众认知。基于此,掌握技术和数据优势的国家可将基于大数据模型发展而来的人工智能与各种网络机器人结合,制造新型“网络水军”,通过混合虚假信息和扭曲事实性信息批量化地炮制丑化他国形象的言论。这不仅直接影响公众舆论和抹黑他国国家形象,更有助于这些国家强化在国际舆论场的主导性与主动权。
After the large-scale application of generative AI as represented by ChatGPT, the public opinion ecosystem will be further complicated and muddied, and the validity and credibility of Internet information will be further reduced. New media gives every individual the right to speak out. The emergence and application of generative AI such as ChatGPT has reduced the information asymmetry among different individuals in the social information field and greatly increased the frequency and weight of individual voices in public opinion. Information entropy in the public opinion field will greatly increase. The social information field and public opinion field further present the features of “multi-centering,” and the government’s authoritative position in information release and public opinion guidance is severely challenged. With the rapid development of generative AI capabilities, the threshold for creating false information such as fake videos will be significantly lowered. AI can use deep fakes to manipulate elections, exacerbate social divisions, and reduce society’s trust in the government. The credibility of such deep fake content is rapidly increasing with the development of AI. Even originally accurate content can be dismissed as deep fake content, directly affecting the credibility and authority of the government. In recent years, fake news circulating on social media has caused much controversy. For example, fake videos of the U.S. president’s speeches are constantly circulating online, causing people to worry about the president’s health. Some videos have even had a direct effect on the battlefield of public opinion. After the widespread use of generative AI developed based on general large models as represented by ChatGPT, more social groups will use this technology to produce videos, charts, and other information. The power to produce highly credible news and information will no longer be concentrated in the hands of the state and mainstream media, and the entities involved in information dissemination will become more diversified. This will further increase the complexity of Internet information and intensify the existing trend towards the fracturing of Internet society. Social groups that have mastered the technology will compete with the state over the right to interpret the truth, and false information that is difficult to identify as such will further reduce the authority and credibility of the news media and even the government.
在以ChatGPT为代表的生成式人工智能大规模应用后,舆论生态将进一步复杂化与浑浊化,网络信息的有效性与可信度将进一步降低。新媒体赋予了每个个体发声的权利。而ChatGPT等生成式人工智能的出现和应用降低了社会信息场域中不同个体的信息不对称状况,大幅提高了个体在舆论场中的发声频率和权重,舆论场中的信息熵将大幅提高,社会信息场和舆论场进一步呈现“多中心化”特征,政府在信息发布和舆论引导等方面的权威地位受到严峻挑战。随着生成式人工智能功能的快速发展,伪造视频等虚假信息的制造门槛将大幅降低,人工智能可以通过深度伪造来操纵选举、加剧社会分裂和降低社会对政府的信任。这些深度伪造内容的可信度随着人工智能的发展快速增强,甚至使原本准确的内容也会被认为是深度伪造后的产物,直接影响到政府的公信力和权威。近年来,社交媒体上流传的假消息已经引起诸多争议。例如,有关美国总统演讲的伪造视频在网上不断流传,引发人们对总统身体健康的担忧,有些视频甚至直接对战场舆论产生影响。在以ChatGPT为代表的基于通用大模型开发的生成式人工智能被广泛运用后,会有更多社会团体通过该技术制作视频、图表等信息,具有高度可信度的新闻与信息的生产权力不再集中在国家和主流媒体手中,信息传播主体变得更加多元,将会进一步提高网络信息的复杂度,加剧原本存在的网络社会撕裂态势,掌握技术的社会团体将与国家展开真相阐释权的争夺,难以辨别的虚假信息将进一步降低新闻媒体乃至政府的权威性与可信度。
In addition, ChatGPT’s “bias amplification” ability will amplify biases and stereotypes in its training data, further marginalizing groups that are already at a disadvantage in society. When using ChatGPT, some users have found it responds to certain questions about Black women by downplaying their contributions, and it sometimes deliberately belittles certain political figures. This is because the data from the current international Internet contains a large amount of biased information. Stereotypes, prejudices, and discrimination have been widely recorded in machine learning methods, and R&D institutions, limited by algorithm capabilities and costs, are unable to completely scrub out such information. Countries with monopoly advantages in international network data management can artificially create “information cocoons” for AI by methods such as inserting malicious information to pollute databases. This will make it so AI develops a thinking framework with ideological and cognitive biases during the training process, affecting its output results and thereby potentially affecting the viewpoints and cognition of users.
此外,ChatGPT具备的“偏差放大”能力,会放大其训练数据中的偏见和刻板印象,使得已处于社会不利地位的群体进一步边缘化,已有使用者在使用ChatGPT时发现,其在回答某些有关黑人女性的问题时会刻意降低她们所作贡献的重要性,有时还会刻意贬低某些政治人物的形象。这是因为当前国际互联网数据中蕴含大量充满偏见的信息,刻板印象、偏见和歧视已在机器学习方法中得到广泛记录,研发机构受限于算法能力和成本难以完全净化此类信息。在国际网络数据管理方面具有垄断优势的国家可以通过插入恶意信息污染数据库等方式,人为制造人工智能的“信息茧房”,使得此类人工智能在训练过程中生成带有意识形态和认知偏见的思维构架,影响其输出结果,进而潜在地影响使用者的立场与认知。
(ii) Data security will be difficult to safeguard, and ideological infiltration methods will grow more diverse
(二)数据安全难以保障 意识形态渗透方式更加多元
With the widespread use of AI based on large models and big data, the risk of leakage of important data of citizens and countries will suddenly increase, causing a sharp increase in security risks. At present, the new generation of AI is made possible by deep learning and operations based on big data. The interactive use of large amounts of sensitive data by AI during deep learning not only exposes the private information of humans to AI, but also greatly weakens the government’s ability to supervise data and information. The political security issues caused by personal information leakage already largely extend beyond the traditional security field. From a government perspective, a national government can quickly improve the efficiency of its information collection and decision-making by using ChatGPT, but this requires the government to “feed” relevant documents and data to ChatGPT so that it can make decisions more in line with actual situations. This undoubtedly increases the risk of national data being stolen: On the one hand, the working mechanism of ChatGPT is still a “black box”, and the possibility that it can store and transmit relevant data during its operations cannot be ruled out. On the other hand, the functionality of ChatGPT enables it to fully understand the relationship between data in a short time through self-supervised learning capabilities. In a feature update in May 2023, OpenAI lifted the restrictions on ChatGPT’s Internet connection capabilities, allowing it to “know” the latest information, using specific third-party software as a springboard. Although it still cannot access certain “security-protected” websites, the unlocking of networking capabilities has strengthened ChatGPT’s deep data retrieval and serialization capabilities. ChatGPT and similar generative AI systems collect and associate targeted large-scale data through keyword reminders and other methods, creating “portraits” of certain events or plans. For example, a country’s government could use this technology to collect targeted information on port shipments and important resource transfers in some other country, using this small window to dynamically perceive the domestic conditions of other countries in order to get an early warning of possible military activities. This would significantly reduce the confidentiality and security of government behavior. Without specific countermeasures, countries weak in S&T will be unilaterally transparent to technologically powerful countries, and technologically powerful countries will always hold the strategic and tactical initiative. The power structure among countries will become more unbalanced, forming a “Matthew effect” in the field of international power.
随着基于大模型和大数据的人工智能的广泛运用,公民和国家重要数据外泄的风险骤然上升,安全风险由此陡增。当前,新一代的人工智能是以大数据为基础开展深度学习和运转的,人工智能在深度学习中对大量敏感数据的交互使用,不仅使人类隐私暴露在人工智能之下,也极大地削弱了政府对数据信息的监管能力,个人信息泄露引发的政治安全问题很大程度也已经超越了传统安全领域。从政府层面看,国家政府能够通过使用ChatGPT来快速提高信息收集和决策效率,但这就要求政府为ChatGPT“投喂”相关文件和数据,使其能作出更符合实际发展的决策,而这无疑加剧了国家数据被盗取的风险:一方面,ChatGPT的工作机制仍是一个“黑箱”,不能排除其在运作过程中会存储与传递相关数据的可能;另一方面,ChatGPT的功能使得其能够在短时间内通过自监督学习能力充分理解数据之间的关系。在2023年5月的功能更新中,OpenAI公司已经解禁了ChatGPT互联网连接能力上的限制,允许其通过特定的第三方软件作为跳板“知晓”最新的信息。尽管它仍然不能访问某些被“安全保护”的网站,但联网能力的解禁强化了ChatGPT拥有的数据深度检索与串联能力。ChatGPT及类似的生成式人工智能通过关键词提醒等方式进行具有针对性大范围的数据收集与联想,对某些事件或计划进行“画像”制作。例如,一国政府可以借助该技术有针对性地收集部分国家的港口运输、重要资源转移情况等,“管中窥豹”地动态感知他国国内状况,从而提前预警可能的战争行为,这将大幅降低政府行为的机密性和安全性。若无特定反制措施,科技弱国将对科技强国单方面透明,科技强国将始终持有策略和战略主动性,国家之间的权力结构将变得更加不平衡,形成国际权力领域的“马太效应”。
From the perspective of user information exchange, the dialogue between users and ChatGPT is not only a process of AI self-reinforcement learning, but also a process of the disclosure of users’ personal information. When a user uses ChatGPT for information query, ChatGPT can learn the user’s speech characteristics, current areas of interest, and even identity through information exchange. In a networkized information society, each citizen’s state of mind, behavioral habits, and characteristics can be obtained through the collection and processing of monitoring data such as their real-time public speech and online behavior. The constant communication between the public and ChatGPT actually gives AI the opportunity to conduct in-depth analysis of user portraits for the group. Language models not only offer the potential to produce lower-cost propaganda, but can also improve the effectiveness of propaganda by tailoring the quality of propaganda to specific groups. Thus, such models can serve as content generators and disseminators for cognitive warfare between states. Through in-depth group portraits, a state is able to “prescribe the right medicine” and carry out ideological subversion using propaganda models that are more familiar and favorable to the target group. In this way, subversive activities transition from a method of “indiscriminate delivery” to one that is “precise and differentiated,” significantly increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of ideological penetration activities. In addition to drawing group portraits, ChatGPT also gives humans the ability to accurately construct portraits of elites. Currently, AI systems are already able to accurately portray the personal images of other countries’ political elites, who are seen as opponents in a strategic game. AI can analyze and grasp the personality traits of political leaders by using their public speeches on different occasions as data. It can even predict the language characteristics of political leaders based on language data. This makes targeted attacks on perceptions of leaders more difficult to defend against.
从用户信息交流层面看,用户与ChatGPT进行的对话不仅是人工智能自我强化学习的过程,更是用户个人信息泄漏的过程。当用户使用ChatGPT进行信息查询时,都能通过信息交流得知用户的言语特征、当下关注重点甚至身份。在网络化信息社会中,每个公民的思想状态、行为习惯和特点都能够通过对其公开言论、网络行为的实时监控等数据的收集与处理获得。而公众与ChatGPT的不断交流,实际上也给予了人工智能对群体用户画像展开深度分析的机会。语言模型不仅提供了生产出更低成本宣传的潜力,还可以通过针对特定群体来调整宣传质量,以提高宣传效能,因而可以成为国家间开展认知战的内容生成器与传播器,国家得以通过群体深度画像“对症下药”,基于目标群体更熟悉和更具好感的宣传模式开展意识形态的颠覆行动,实现颠覆活动从“无差别投送”向“精确且有差别”方向的转变,意识形态渗透活动效能与效率大幅提高。除对群体画像的刻画外,ChatGPT也赋予人类精准刻画精英画像的能力。当前,人工智能系统已能实现对作为博弈对手的他国政治精英个人形象的精准刻画。人工智能可以根据政治领导人在不同场合下对外演讲的材料,分析与把握领导人的性格特质,甚至能够基于语言材料预测政治领导人的语言特点,这使对领导人认知的针对性攻击将会变得更加难以防御。
(iii) The imbalance in power development among countries will further increase, intensifying changes in domestic and international power structures
(三)进一步加大国家间实力发展的不平衡 国内国际权力格局变动加剧
With the in-depth development of AI technology, the existing competition among technological powers will further intensify. Changes in AI technology will further consolidate the power of the pioneer countries to develop technology in the knowledge field, and the control of this power by major countries will become more invisible and natural. When a certain party’s AI research achieves a breakthrough in algorithms or computing power, this advantage can spill over to other fields, empowering rapid breakthroughs and development in other technologies. Therefore, the cross-field application of such technology will lay down rules for the research ideas of others, and latecomers will rely on this path of research. The dominant party can therefore dominate and formulate the rules and discourse in the general large model research and application fields. At present, the exponential development trend in AI performance is rapid and sustained once it gets going. It is easy for those with advantages in research to transform their algorithm and computing power advantages into an insurmountable superiority over disadvantaged parties, and gain most of the fruits of development. This creates a “winner takes all” situation. Such technological progress will ultimately create winners and losers at the national level. Especially at this critical moment when the international power structure is changing, breakthroughs brought about by technological changes will be regarded by all parties engaged in competition as the “key” to winning the contest. This will inevitably result in more intense, zero-sum competition between different countries or political alliances in this field. Today, the Group of Seven has reached a consensus through the establishment of the “Hiroshima AI Process” in an attempt to “preemptively” seize the leading voice in the international discourse around issues such as suitable values for AI. This means that the establishment of organizations such as transnational data alliances and algorithm alliances may become an important strategy for S&T competition among countries. Technology and data protectionism centered on big models, big algorithms, and big data will become the core content of S&T competition among major powers. International confrontation situations such as S&T blockades and even S&T cold wars may become new trends in international competition.
随着人工智能技术的深度发展,技术大国之间的原有竞争态势将会进一步激化。人工智能技术的变革会进一步巩固知识领域中技术先发国的权力,大国对权力的控制变得更加隐形且自然。当某一方的人工智能研究实现算法或算力的突破,其能将这种优势外溢到其他领域,赋能其他技术快速突破发展。而这种技术的跨领域应用会规制他者的研究思路,后来者会依赖这种研究路径,优势方因而能够掌握对通用大模型研究和应用领域的规则以及话语主导权与制定权。当前,人工智能效能的指数级发展态势,呈现出“一步快、步步快”特点,研究优势方很容易将算法和算力优势转化为对其他劣势方的碾压态势,获得大部分的发展成果,形成“赢者通吃”的局面, 此类技术进步最终在国家层面会制造赢家和输家。特别是当下正处于国际权力格局变动的关键时刻,技术变革带来的突破将会被竞争中的各方视为赢得竞赛的“钥匙”,这就造成不同国家或政治联盟必将在此领域展开更激烈、零和性的竞争。如今,七国集团已就建立“广岛人工智能进程”达成共识,试图“先发制人”抢夺人工智能适用价值观等方面的国际话语权。这意味着组建跨国数据联盟、算法联盟等组织可能会成为国家间展开科技竞争的重要方略,以大模型、大算法和大数据为核心的技术与数据保护主义将成为大国科技竞争的核心内容,科技封锁乃至科技冷战等国际对抗态势可能将成为国际竞争的新态势。
The first feature is that unbalanced S&T development will worsen the “Matthew Effect” in the development among countries, making it more difficult for developing countries to change their disadvantaged position in the global economic system. The capitalist global economy is based on a worldwide division of labor, with different actors assuming different economic roles. The advantages of developing countries participating in the global economic system are mainly their relatively low labor costs and ample supply of natural resources. However, in the AI era, there is a possibility and tendency for peripheral areas to be permanently marginalized. Although generative AI can significantly improve the efficiency of industrial production and experimental R&D, many developing countries lack the digital infrastructure needed to power AI, the innovation environment needed to build new models that utilize AI, and the skills to fully utilize its power. This means that these countries can only continue to be forced to accept industries transferred to them from developed countries. Generative AI has extremely high requirements for cumulative training and infrastructure, which determines that the R&D and application of this technology have cumulative features. Long-term investment is needed to achieve in-depth research and development of the technology. This makes it difficult for other countries, especially countries under chip import and export restrictions, to achieve “overtaking on the curve” (弯道超车, using new opportunities to overtake current leaders), widening the “rich-poor gap” among countries in the development of AI industries. The replacement of labor by AI technology has further diluted the demand for labor in the capitalist economic system, while the development of the AI industry has not yet created new labor positions. This has further weakened the relative advantages of developing countries, and their relative position in the global economic system is further shifting to the periphery. Countries with advantages in technology and capital can build a “center–periphery” economic and S&T development structure for the new era, relying on their advantages in the development of AI technology to continuously strengthen their core position in the economic and S&T research fields. Meanwhile, countries at the periphery of the structure will be stuck with the choice of obtaining some core technologies through exchanges with and learning from core S&T countries in order to promote the upgrade of their national industrial structure, or else continuing to receive industries transferred from developed countries. The former choice means that peripheral countries will continue to strengthen their dependence on central countries, making it more difficult to break out of the system structure that exploits them. The latter choice means that relatively underdeveloped countries will miss out on the wave of cutting-edge technology R&D and applications, and their development potential will be further reduced, ultimately leading to the further expansion of the gap created between countries by the “Matthew Effect.”
第一个特征是,科技发展不平衡将恶化国家间发展的“马太效应”,发展中国家在全球经济体系中的不利地位更加难以改变。资本主义世界经济以世界范围内的劳动分工为基础,不同行为体承担不同的经济角色。发展中国家参与世界经济体系的优势主要是相对低廉的劳动力成本和充足的天然资源供给,但在人工智能时代出现了边缘地区被永久边缘化的可能和倾向。尽管生成式人工智能能够大幅度提高工业生产与实验研发效率,但许多发展中国家缺乏为人工智能提供动力所需的数字基础设施、建立利用人工智能的新模型所需的创新环境以及充分利用其力量的技能,意味着这些国家只能继续被迫接受来自发达国家的产业转移。生成式人工智能对训练积累和基础设施的极高要求决定了该技术的研发和应用具有累积性特征,必须依赖长期投入才能够实现技术的深度研发,使得其他国家特别是芯片进出口受限国家难以实现“弯道超车”,加大了国家间人工智能产业发展的“贫富差距”。而人工智能技术对劳动力的替代进一步稀释了资本经济体系对劳动力的需求,人工智能产业的发展暂时也没有实现创造新的劳动岗位, 这使得发展中国家拥有的相对优势进一步被削弱,在世界经济体系中的相对位置进一步向边缘推移,技术和资本占据优势的国家能够据此构建新时代的“中心—外围”经济与科技发展结构,凭借其在人工智能技术发展上的优势不断强化在经济和技术研究领域的核心地位;而处于边缘结构的国家将陷入选择在与核心科技国家的交流学习中获得部分核心技术来推动国家产业结构的升级,或者继续维持承接发达国家转移产业的抉择中。前者意味着边缘国家将继续强化对中心国家的依赖,更加难以突破体系结构对其的剥削;后者则代表发展相对落后国家将错失对前沿技术研发和应用的浪潮,发展潜力将会被进一步缩减,最终导致国家之间发展“马太效应”的进一步扩大。
The second feature is a further enhancement of the power of non-state actors and a trend toward the “multi-centering” of political power. Big data, algorithms, and even AI, while bringing profound changes to society, are also becoming effective means for platform companies to capture power. Core technologies such as the learning iteration of generative AI are mainly in the hands of S&T giants such as Google and Microsoft. Such ownership will give rise to a group similar to a “transnational S&T community.” The information monopoly of S&T companies gives them power over the acquisition and interpretation of information. The originally relatively stable boundaries of power between sovereign states, especially in terms of power to produce public goods, will become blurred or even disappear due to the arrival of new entities. The data training and algorithms used for the update and iteration of ChatGPT and other similar generative AI are mainly in the hands of large technology companies, especially Internet companies, and groups of scientists, so it is difficult for the government to get involved. Moreover, the broad application prospects of generative AI in many fields allow S&T companies to participate in national affairs and share some power, which in turn creates the possibility for these companies to intervene in or even dominate affairs over which the state originally had a monopoly of power. Through long-term investment, technology R&D, and the practical application of research results, S&T giants will assume the role of producing and providing public goods in many areas of society. Therefore, in some fields such as economic and social management, the right to supply public goods will to a certain extent be transferred from the traditional political authority held by nation-states to the power of capital. Government power will be further differentiated, and the disconnect between technical authority and bureaucratic authority may gradually erode the effectiveness of the national government’s actions and allow national power to be “hijacked” by S&T companies.
第二个特征是,非国家行为体权力进一步增强,政治权力呈现“多中心化”趋势。大数据、算法乃至人工智能,在给社会带来深刻变革的同时,也正在成为平台公司捕获权力的有效手段。生成式人工智能的学习迭代等核心技术主要掌握在谷歌和微软等科技巨头手中,此类拥有权将催生出一种类似“科技跨国共同体”的团体,科技企业的信息垄断给予其左右信息获取和诠释的权力。原本相对稳定的主权国家间的权力边界,特别是对公共产品的生产权力将由于新主体的加入而变得模糊不清甚至消失。ChatGPT等类似的生成式人工智能的更新迭代所依赖的数据训练和算法等主要都掌握在大型技术企业特别是互联网企业与科学家团体手中,政府很难插足,而生成式人工智能在多领域的广泛运用前景使得科技企业得以参与国家事务并分享部分权力,进而让这些企业存在干预甚至主导原本国家垄断权力事务的可能性:科技巨头通过长期投资、技术研发与成果转换,在很多社会领域担负起生产与提供公共产品的职能。因此在经济与社会管理等部分领域,民族国家掌控的传统政治权力会在一定程度上向资本权力让渡公共产品的供应权,政府的权力将会被进一步分化,技术权威与官僚权威之间的不同步可能会逐步销蚀国家政府的行为效果,国家权力可能会被科技企业“绑架”。
(iv) Generative AI will enable battlefield weapons, turning the cognitive battlefield into an important area of contest
(四)生成式人工智能赋能战场武器 认知域战场成为重要博弈场域
Technical equipment equipped with new types of AI will significantly affect and change the current battlefield situation. AI has been called the third revolution in warfare, following the invention of gunpowder and the atomic bomb. ChatGPT’s high adaptability and powerful information processing and output capabilities give it broad prospects for battlefield applications. The CIA is currently discussing how to use ChatGPT and similar programs to assist in intelligence collection and espionage operations. The large-scale application of ChatGPT and similar AI in military operations will greatly enhance military capabilities. In terms of battlefield target recognition and combat information processing, ChatGPT can be loaded onto drones and military equipment to perceive battlefield information in real time. Recognition networks equipped with the GPT-4 model can effectively improve the accuracy of target recognition in complex environments, greatly improving the combat effectiveness of drones. ChatGPT can also efficiently connect different battlefield information perception systems in series to create intelligence-sharing terminals through perception, aggregation, processing, and output methods. AI based on the GPT model architecture can continuously filter large volumes of battlefield information and data and flag its important content, improving the efficiency of manual information processing and analysis and providing command departments with accurate information and data and decision-making bases. In terms of battlefield command, combat command systems controlled by generative AI have faster response rates, higher-level decision-making, and more outstanding efficiency compared to traditional command systems. In the face of increasingly complex battlefield formats and exponential growth of battlefield information, generative AI based on big data technology and trained on military decision-making styles can efficiently analyze the combat needs of commanders and provide highly accurate risk assessment and decision-making suggestions through large-scale model processing, combat simulation, and deduction based on war game deductions, helping commanders discover and defeat threats before they arise and greatly improving the level of ad hoc decisionmaking on the battlefield. In terms of logistics, ChatGPT can be combined with technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing to dynamically monitor the use and deployment of strategic military materials. It can improve warehouse management efficiency by analyzing data such as the quantity of stored materials and maintenance status, achieving a dynamic balance between demand and resource transportation to provide optimal logistics supply solutions. Therefore, when ChatGPT is applied in the combat field, it will significantly raise the military’s intelligentized information acquisition and decision-making level. The military’s combat capabilities are closely linked to the intelligentization level of its equipment. Battlefield information collection and decision-making methods will transform by moving in the direction of “cloud collection” and “AI decision-making.”
搭载新型人工智能的技术装备将显著影响和改变目前的战场态势。人工智能被称为是在火药和原子弹发明之后的第三次战争革命,ChatGPT的高度可适配特征与强大的信息处理和输出能力使其在战场应用方面拥有广泛前景。美国中央情报局就在讨论如何运用ChatGPT及类似程序辅助开展情报收集和间谍等业务。在军事行动中大规模应用ChatGPT及类似人工智能将大幅提升军队能力。在战场目标识别和作战信息处理方面,ChatGPT能装载到无人机、军用器械上用以实时感知战场信息,搭载GPT-4模型的识别网络能够有效提升在复杂环境中对目标的识别精度,更能大幅度提高无人机的作战效能。ChatGPT还能高效串联不同战场信息感知系统,通过感知、汇总、处理及输出的方式打造情报共享终端,基于GPT模型构架的人工智能能够持续不断地过滤大量战场信息数据并标注其重要内容,提高人工信息处理和分析的效能,为指挥部门提供精确的信息数据和决策依据等。在战场指挥方面,生成式人工智能控制的作战指挥系统相较传统指挥系统的反应速率更快,决策水平更高,效能更加突出。面对日益纷杂的战场形态和指数级增长的战场信息,基于大数据技术和军队决策风格训练的生成式人工智能可以高效分析指挥人员的作战需求,通过大模型的处理和战斗模拟、兵棋推演等方式提供高精确度的危险评估和决策建议,帮助指挥者在威胁产生前发现并挫败威胁,大幅提高战场临时决策的水平。在后勤物流方面,ChatGPT搭配物联网和云计算等技术动态监测军事战略物资的使用和调配情况,通过对储存物资数量、保养情况等数据的分析提升仓库管理效能,实现需求与资源运输间的动态平衡,为后勤补给提供最佳方案。因此,ChatGPT应用于作战领域后将大幅提升军队的智能化信息获取和决策水平,军队作战能力与装备的智能化水平紧密挂钩,战场的信息收集和决策方式向“云端收集”“人工智能决策”方向转变。
The emergence of ChatGPT will also highlight the importance of cognitive confrontation capabilities between states. New cognitive warfare and information warfare weapons developed based on generative AI, big data, and big algorithms may reduce trust between countries. NATO’s cognitive warfare doctrine holds that victory is defined more by capturing the psychological and cultural high ground than the geographical high ground. Cognitive warfare is highly dependent on support from network information technology and social media platforms. Social media platforms and networks not only give each individual the ability to obtain information and communicate instantly, but they have also become important platforms from which hostile countries launch targeted attacks. Such attacks can be divided into cognitive attacks, such as transmitting false battlefield information and fake speeches by leaders, and information attacks such as destroying other countries’ information transmission systems and intercepting and deciphering information transmitted by other countries. In these areas, generative AI will become a powerful tool for cognitive warfare: After attack information is processed by generative AI, its capabilities for concealment and deception will be greatly improved, gradually giving cognitive warfare the features of “highly interactive, occurring throughout all time and space from multiple perspectives.” The military can train generative AI to continuously strengthen its capabilities in the production and delivery of false information. It can intensively carry out multi-angle information bombing and emotional incitement on the opponent’s people through AI generated images of battlefield witnesses and victims. Through continuous interaction and communication with the public, it can continuously indoctrinate people with falsified facts and create targeted information fog, which in turn can generate war-weariness and anti-war sentiment in other countries and threaten the stability of public opinion in the domestic societies of other countries, ultimately overcoming the opponent’s will to resist. At the same time, generative AI can launch non-stop information bombing against the enemy’s information receiving systems, affecting the normal operation of the enemy’s network technology facilities, cutting off the enemy’s information reception, and reducing the efficiency of internal communication within the enemy’s military. Therefore, the outstanding performance of generative AI in cognitive warfare may aggravate public opinion relations between countries. Every country will always be on guard against possible disinformation attacks and tend to blame any disruptions arising from public opinion within society on the actions of other countries, especially enemy countries. This will further weaken the foundation of strategic mutual trust between countries.
ChatGPT的出现还将突出国家认知对抗能力的重要性,以生成式人工智能和大数据、大算法为理论基底开发的新型认知战、信息战武器可能会降低国家间的互信。北约认知战学说认为,胜利更多地根据占领心理文化而非地理制高点定义。而认知战高度依赖网络信息技术和社交媒体平台的加持。社交媒体平台与网络不仅给予每个个体获取即时信息和交流的能力,也成为敌对国家展开针对性攻击的重要平台。这种攻击可分为传递虚假战场信息、伪造领导人发言等认知攻击和摧毁他国信息传递系统、阻截与破译他国传递信息等信息攻击。在这些方面,生成式人工智能将成为认知战的强大工具:攻击信息在被生成式人工智能处理后,其隐蔽性和欺骗性将大幅提升,使得认知战逐步呈现“全时空、多角度、强互动”的特点。军队可训练生成式人工智能,不断加强在虚假信息的制作与投放方面的能力,通过扮演战场亲历者、受害者等形象向对方民众密集地展开多角度的信息轰炸和情绪煽动,通过与民众的不断互动交流持续灌输伪造事实,打造具有针对性的信息迷雾,进而在他国催生厌战反战情绪,威胁他国国内社会民意稳定,最终击垮对手的抵抗意志。同时,生成式人工智能针对敌方部队的信息接收系统展开不停歇的信息轰炸,影响敌方网络技术设施的正常运营,切断敌方部队的信息接收,降低敌方军队内部沟通效能。因此,生成式人工智能在认知战中的突出表现可能会让国家间舆论关系变得更加紧张。每个国家都在防御可能的虚假信息攻击,并倾向于将社会内部出现的舆论乱象归咎于他国特别是敌国的作为,各国间的战略互信基础将会进一步削弱。
(v) ChatGPT training and operations will impact existing legal requirements and significantly lower the threshold to crime
(五)ChatGPT训练与运转冲击现有法律规定 犯罪门槛大幅降低
At present, the party who is responsible for materials related to ChatGPT is not clear, and ChatGPT can easily infringe on the rights of others during training and use. As a very large model with more than 100 billion parameters, ChatGPT cannot provide a clear logical reasoning process and clear data source for each decision or output result produced during its operation. Even the “real” sources it provides may be accompanied by real details and false citations. When an accident results from the use of the output results of generative AI, there is no clear subject who can bear this part of the responsibility. Considering this issue, the U.S. Supreme Court once discussed the entities liable for AI chatbots, and one justice suggested that “the legal protections that shield social networks from user content lawsuits may not apply to AI-generated work.” At the same time, the large amount of data used to train ChatGPT means that it is difficult to prevent the theft and misuse of personal information, significantly increasing the risk of data leakage. It is difficult for the existing legal system to restrict related behaviors. The capabilities of generative AI such as ChatGPT come from the capture and learning of massive data, but this involves issues such as whether the behavior of capturing data is compliant with laws and whether the captured data will be used for other purposes. It is also difficult to verify the legality and validity of data sources. This is deeply related to the legality of the source of generative AI capabilities. In addition, the training and operation methods of ChatGPT undermine the public’s informed consent mechanism, in that data capture is carried out by S&T companies without individual consent, making it difficult for the public to protect the privacy of personal data. It is even difficult for citizens to detect the leakage of their private personal data. Payment information, addresses, taxi records, and even chat records may be easily obtained by others due to program design flaws and widespread user use, making it increasingly difficult to protect the privacy of information. In addition, the relevant companies are not transparent about the procedures used to process training data. Personal information and confidential government information may not be fully processed before being used directly for training. After the training, the relevant data may also be deliberately retained by the company, increasing the possibility of data leakage.
目前,有关ChatGPT的责任承担者不明晰,训练和使用过程中易侵犯他人权利。ChatGPT作为拥有超过千亿参数的超大模型,在运转时它并不能给其每个决策或输出结果一个清晰的逻辑推理过程和明确的资料来源,甚至其提供的“真实”资料来源也有可能附有真实的细节和虚假的引用。而一旦人们在使用生成式人工智能的这些输出结果时导致事故,却没有明确的主体能够承担这部分责任。考虑到此问题,美国最高法院曾就人工智能聊天机器人的主体责任问题展开讨论,有大法官就建议“保护社交网络免受用户内容诉讼的法律保护措施可能并不适用于人工智能生成的工作”。同时,ChatGPT训练所使用的大量数据使得个人信息被窃取盗用的情况难以避免,数据泄露风险大幅提高,现有法律体系很难限制相关行为。ChatGPT等生成式人工智能的能力源自对海量数据的抓取与学习,但这涉及抓取数据这一行为是否合规、抓取的数据是否会另作他用等问题,数据来源的合法性与有效性也难以验证,这深度关系到生成式人工智能能力来源的合法性。此外,ChatGPT的训练和运转方式损害了公众的知情同意机制,即科技企业不经个人同意而开展的数据抓取使得公众对个人数据隐私的保护难以落实,公民甚至都难以察觉个人隐私数据的泄露。支付信息、地址、打车记录甚至聊天记录都有可能因为程序设计缺陷和用户的广泛使用被他人轻易获取,信息隐私保障愈发困难。相关企业对训练数据的处理工序也不透明,个人信息和政府机密信息可能并没有被充分处理便直接用于训练,训练结束后相关数据也可能会被企业刻意保留,加大了数据泄露的可能性。
At the same time, the widespread use of generative AI will lower the threshold for cybercrime and make it more difficult to track criminal behavior. Europol believes that ChatGPT is a valuable resource for potential criminals who lack the technical knowledge to generate malicious code. As a conversational AI, ChatGPT can quickly produce the required type of code and generate programs based on user requirements, making it a natural criminal tool when in the hands of criminals. Although each company currently claims to have set up a program for rejecting inappropriate requests for its artificial intelligence products, the current programs do not yet have the ability to identify the deeper intentions behind requests, and users have still found that they can “trick” the program during use to achieve their purposes. At the same time, generative AI has the ability to edit batches of text and forge pictures and videos on a large scale. Criminals can combine these capabilities to carry out telecommunications fraud and other activities in a way that better aligns with cultural and social characteristics, so that their tactics are more “authentic” and “effective.” Criminals can take advantage of information gaps to create scams that are more in line with logic and strike at the weakness of people who lack the ability to discern information. The frequency and success rate of these crimes will increase significantly.
与此同时,对生成式人工智能的广泛使用将降低网络犯罪门槛,犯罪行为追踪难度加大。欧洲刑警组织认为,对于缺乏技术知识的潜在罪犯来说,ChatGPT是生成恶意代码的宝贵资源。ChatGPT作为对话式人工智能,它可以基于用户要求快速产出所需类型的代码和生成程序,这为犯罪分子提供了天然犯罪工具。尽管当前各家公司都宣称为旗下的人工智能产品设置了拒绝不适当请求的程序,但当前程序尚不具备深度识别需求背后意图的能力,仍有使用者发现在使用过程中能够“欺骗”程序来达到目的。同时,生成式人工智能已具备批量文案编辑、伪造图片和视频的能力,犯罪分子结合这些能力开展的电信诈骗等活动更加符合文化与社会特征,更具“真实性”与“有效性”。犯罪分子得以利用信息差营造更符合逻辑的骗局,对缺少信息辨别能力的人“降维打击”,犯罪频率与成功率都将大幅上升。
(vi) ChatGPT will bring about structural unemployment, affecting the labor market and social stability
(六)ChatGPT带来结构性失业现象 影响劳动力市场及社会稳定
As an important component of national security governance efforts, employment risk governance is embedded in the system of national development practices. This technological revolution, represented by AI, may bring about many types of unemployment. ChatGPT and other generative AI will permanently replace some jobs in certain industries, posing the risks of collective and long-term unemployment risks to social development. As a new productivity tool, ChatGPT will inevitably have a severe impact on the current ways in which people work and the balance of supply and demand in the labor market. Companies can quickly obtain and extract information through generative AI such as ChatGPT. For example, OpenAI Codex, which is based on the GPT-3 model, is proficient in more than a dozen programming languages and improves programmers’ efficiency through “memorizing code”. Generative AI has also greatly improved the productivity and creativity of the workforce. Low-skilled workers can use tools such as ChatGPT to narrow the gap in work quality between themselves and high-skilled workers.
就业风险治理作为国家安全治理事业的重要组成部分,内嵌于国家发展的实践体系中。此次以人工智能为代表的技术革命可能将带来多类型的失业现象,ChatGPT及其他生成式人工智能将永久性地取代某些行业的部分岗位,对社会发展带来群体性和长期性失业风险。ChatGPT作为全新生产力工具,必然对当前人们的工作方式和劳动力市场的供需平衡产生剧烈冲击。公司可通过ChatGPT等生成式人工智能对信息进行快速获得和提取,例如,基于GPT-3模型产生的OpenAI Codex精通十几种编程语言,通过“背代码”方式以提高程序员工作效率。生成式人工智能还大幅提高了劳动力的生产效率与创造力,低技能工人则能通过使用ChatGPT等工具缩小他们与高技能工人之间工作质量的差距。
However, the substantial improvement in productivity also means that the labor force required for existing jobs will be reduced, as well as the demand for manual workers and workers doing basic intellectual work, and it will be possible to replace some repetitive labor and creative work with generative AI. From the perspective of economic development, the development and application of disruptive and breakthrough technologies will affect the existing economic format and economic distribution relations, reshape the current employment and social and economic pattern, and produce destructive substitution effects on existing technical groups. A report released by OpenAI in March 2023 shows that approximately 80% of the U.S. workforce will see some of their work tasks affected by GPT models and related technologies. A report released by Goldman Sachs shows that, at present, about 2/3 of the jobs in the United States and Europe are “affected to some extent by AI automation,” and as many as 1/4 of the jobs can be completely performed by AI. Different from the replacement of low-end manufacturing jobs by AI of the past, the job positions that generative AI can handle are more concentrated among positions where similar operating rules and procedures are applied and that require frequent processing of large amounts of similar data. These behaviors can be easily completed through generative artificial intelligence. For example, you only need to input basic news copywriting rules and information capture procedures into generative AI, and it can automatically capture news data and “fill” it into a manuscript, greatly reducing the time required for news writing. Therefore, the widespread use of generative AI such as ChatGPT in these fields will reduce corporate operating costs while improving operational efficiency. The main production entities in this field will shift from humans to AI, and some workers doing intellectual tasks will lose employment opportunities. At the same time, we should also note that the current ChatGPT is a milestone in the development of generative AI, but it is by no means the end of that development. In the future, generative AI may serve as the “control console” and “core brain” of other AI technologies or industrial technologies. Besides some positions that require innovative thinking or subjective adaptability, most fields will see the introduction and dominance of production entities based on generative AI, unleashing an unpredictable surging tide of labor unemployment.
但是,工作效率的大幅提高也意味着既有工作所需劳动力将减少,体力劳动者及部分简单脑力劳动者需求量将大幅度下降,部分重复性劳动和创造性工作存在被生成式人工智能替代的可能。从经济发展的角度看,颠覆性和突破性的技术发展与应用都会影响既有的经济形态和经济分配关系,重塑当前就业和社会经济的格局,对原有的技术人群产生破坏性的替代效应。OpenAI公司2023年3月发布的报告显示,大约80%的美国劳动力会有部分工作任务受到GPT模型和相关技术带来的冲击。而高盛公司发布的报告则表明,美国和欧洲目前约有2/3的工作“在某种程度上受到人工智能自动化的影响”,并且多达1/4的工作可以完全由人工智能完成。 不同于以往人工智能对低端制造业岗位的替代,生成式人工智能可胜任的岗位更多集中在拥有类似运作规则和运转步骤,需要频繁处理大量相似数据的岗位,这些行为都能轻易通过生成式人工智能完成。如只需将基本新闻文案规则与信息抓取程序输入到生成式人工智能中,它就能自动地抓取新闻数据“填写”到文稿中,大幅节省新闻撰写所需的时间。因此,ChatGPT等生成式人工智能在这些领域的广泛使用将在降低企业运营成本的同时提高运营效率,该领域的生产主体从人类转向人工智能,部分脑力劳动者将会因此失去就业机会。同时我们还应注意到,当前的ChatGPT是生成式人工智能发展的一个里程碑,而绝非发展的结束。未来生成式人工智能可能将作为其他人工智能技术或者工业技术的“操纵台”和“核心大脑”,除了部分需要创新性思维或者主观应变能力的岗位外,将有更多领域被以生成式人工智能为核心的生产主体介入和主导,不可预期的劳动力失业潮将汹涌而至。
An organized schematic of the impact of ChatGPT on national security is shown in Figure 2.
ChatGPT对国家安全的相关影响整理如图2所示。
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of ChatGPT’s impact on national security
图2 ChatGPT影响国家安全的示意图


III. Strategies to cope with the new security situation
三 新安全形势下的应对策略
The emergence of ChatGPT poses unprecedented challenges to national security. At the domestic level, ChatGPT impacts existing legal norms and ethics, affects the labor market, and influences ideological stability. At the international level, this technology will affect the dynamics of S&T competition in the international community and impact the international power structure. Needless to say, we can say these challenges are massive, or even disruptive. Therefore, we must prepare for a rainy day and make corresponding preparations in advance, strengthen international cooperation in the construction of innovation systems, and work hard to improve laws and regulations in order to lay a solid foundation for safeguarding China’s national security in the ChatGPT era.
ChatGPT的出现对于国家安全造成了前所未有的挑战。在国内层面,ChatGPT冲击既有法律规范和伦理道德,影响劳动力市场,影响意识形态稳定。在国际层面,该技术将影响国际社会的科技竞赛态势以及冲击国际权力格局。毋庸讳言,这些挑战可以说是巨大的甚至是颠覆性的。因此,我们必须未雨绸缪,提前做好相应准备,在创新体系建设中加强国际合作,在完善法律法规等领域下足功夫,为在ChatGPT时代维护中国国家安全夯实基础。
(i) Internally, we must accelerate the construction of an open, collaborative, and diversified AI innovation system.
(一)对内加快构建开放协同多元的人工智能创新体系
First, we can establish decision-making institutions including an AI development committee to solve the issue of an overall governing force in the AI field. Official departments such as the Ministry of Science and Technology and big data administration bureaus can coordinate the development pace of technology-based enterprises and promote the improvement of China’s general large model R&D and innovation capabilities. The development of existing S&T enterprises currently focuses more on technology R&D and application centered on market competition, with investment in applications far exceeding investment in basic theoretical research. The situation of internal competition hinders improvements in technological innovation and application capabilities. Therefore, taking accelerating basic theoretical development and breakthroughs in major technological applications as our point of departure, we should innovate the technology R&D and application paths of existing enterprises and universities. Based on the diverse and interconnected characteristics of general large model R&D, we should fully realize the interaction and collaboration between various entities and levels in the R&D and application chain to improve our original innovation capability in the general large model R&D system. We should focus on solving the pain points and difficulties in the development of general large models and accelerate the pace at which we are catching up with international leaders.
首先,可以建立包括人工智能发展委员会在内的决策机构,解决在人工智能领域“九龙治水”的局面,通过科学技术部、大数据管理局等官方部门统筹技术型企业发展步伐,推动中国通用大模型研发与创新能力的提高。现有科技企业发展更多是围绕市场竞争进行技术研发和应用,对应用层面的投入远超对基础理论研究投入,自我内耗的竞争形势阻碍了技术创新和应用能力的提高。因此,从加快基础理论发展和重大技术应用突破的角度入手,必须革新现有企业和高校的技术研发和应用路径,基于通用大模型研发中的多元互联特征,充分实现研发和应用链中各主体、各层次之间的互动协同,以提高通用大模型研发体系的原始创新能力,重点攻关通用大模型发展的痛点难点,加快追赶国际先进水平的步伐。
From the perspective of lateral R&D, the government should strengthen support for basic research, especially model data training, and use tax subsidies and other preferential policies to encourage enterprises to make incubation investments around basic theoretical research. Entities such as technology enterprises, universities, and governments play complementary roles: Different enterprises can integrate their data resources, build shared open-source databases and computing engines, reduce barriers to entry by evenly sharing scientific research costs, facilitate large model training for innovative S&T companies, and build a technology R&D model in which “the government provides basic support, multiple parties share responsibilities, and enterprises verify.” In view of the difficulties in the development of existing large models, enterprises and universities should set up key joint research teams to explore the feasibility of different solutions and paths through long-term research. We should leverage the capabilities of S&T companies to convert research results into applications in order to quickly verify technical paths, thereby breaking through the obstacles to the development of large models. From the perspective of vertical applications, entities up and down the production chain should orient themselves to the actual application needs of society, give full play to the multi-modal application capabilities of general large models, create innovative application solutions based on large model capabilities, and quickly realize good iteration and upgrade of application capabilities through methods such as research and interactive feedback. The government should collect opinions from experts and scholars, set up “test fields” for the conversion of technology into applications around key application scenarios, continue to empower enterprises to conduct large-scale experiments on applications, innovate practices for generative AI operations, achieve the integration of the needs of generative AI technology and the current needs of social development, and accelerate the innovative application of generative AI in multiple fields.
从横向研发角度看,政府须强化对基础性研究特别是模型数据训练方面的支持力度,通过税收补贴等优惠政策鼓励企业围绕基础理论研究进行孵化性投入。科技企业、高校和政府等主体发挥互补性作用:企业间可以整合数据资源,构建共享的开源数据库与算力引擎,通过平均科研成本降低准入门槛,为科技创新企业的大模型训练提供便利,构建“政府兜底、多方共担、企业验证”的技术研发模式。而针对现有大模型发展的难点,企业与高校设立重点联合研究团队,通过长期研究探寻不同解决路径的可行性,借助科技企业的转化能力快速验证技术路径,以突破大模型发展阻碍。从纵向应用角度看,产业链上下游应以社会实际应用需求为导向,充分发挥通用大模型的多模态应用能力,基于大模型能力创新应用方案,通过调研和互动反馈等方式快速实现应用能力的良性迭代与升级。政府通过向专家学者征集意见,围绕重点应用场景设立技术转换的“试验田”,不断放权企业展开应用的大规模实验,创新生成式人工智能的运用实践,实现生成式人工智能技术与社会现实发展需求的结合,加快推进生成式人工智能在多领域的创新应用。
In addition, we should gradually reform the talent training model and delivery system, build a high-tech talent cultivation alliance linking universities, research institutes, and enterprises, and provide more intellectual support for generative AI R&D. Talent is the first resource, and the technological innovation system cannot operate without the support of talents. With the explosive rise of ChatGPT, the demand for talents studying the training and application of general large models has surged. However, China still has a large gap in research-type talent in the field of the development of general large models, with a shortfall of nearly 30 million relevant talents. Therefore, in order to promote the rapid development of generative AI, it is necessary to speed up the cultivation of domestic talent.
其次,逐步改革人才培养模式与输送体系,建设高校、研究所、企业三体联动的高新技术人才培育联盟,为生成式人工智能的研发提供更多智力支撑。人才是第一资源,技术创新体系的运转不能缺乏人才支撑。随着ChatGPT的爆火,对研究通用大模型训练和应用的人才需求激增,但当前中国在研发通用大模型方面仍然存在较大的研究型人才缺口,相关人才的缺口接近3 000万。因此,为推动生成式人工智能的快速发展,就必须加快国内人才的培育速率。
The education system, led by universities, should gradually expand the scale of AI research and development majors, subdivide the research directions of these majors, increase the cultivation and application conversion courses on general large model training, and improve the basic AI literacy of school students. At the level of high-quality talent delivery, universities can directly connect with enterprises and research institutes and regularly push high-quality talents to existing AI R&D and application systems through the establishment of joint internship mechanisms.
以高校为主导的教育体系应当逐步扩大人工智能研发专业规模,细分专业研究方向,增加通用大模型训练的培育和转化应用类课程,提高在校学生在人工智能方面的基本素养。在高素质人才输送层面,高校可与企业和研究所直接对接,通过设立联合实习机制,定期推送高素质人才到既有人工智能研发和应用体系。
The government and enterprises should increase their support for relevant talents, attract top talents in relevant fields, selectively introduce some teams of outstanding scientists, and directly enhance the country’s innovation and research capabilities in this area. For example, the government can include talents in the purification of general large model training data and model applications in the existing overseas high-level talent recruitment plan requirements, and by setting up admission criteria and graded benefits, continuously find and attract high-quality overseas talents to return to China to advance their careers. Objectively, there is still a large gap between China and foreign countries in terms of large models and other technologies. Attracting overseas talents should become an important means of quickly improving R&D capabilities. To this end, we should break down ideological constraints, recruit talents with a more open and inclusive attitude, and build a solid talent foundation for the development of AI in China.
政府和企业应加大对相关人才的支持力度,形成对相关领域顶尖人才的吸引力,选择性地引入部分优秀科学家团队,直接提升国家在此方面的创新与研究能力。例如,政府可将通用大模型训练数据的净化与模型应用等方面的人才纳入既有海外高层次人才引进计划需求中,通过设立准入标准和待遇分级,持续性挖掘与吸引海外优质人才回国发展。客观来说,国内外在大模型等技术方面的差距仍然较大,对海外人才的吸引应成为当前快速提高研发能力的重要途径。为此,我们应当打破思想禁锢,以更加开放包容的心态引进人才,为中国人工智能发展筑牢坚实的人才基础。
(ii) Externally, we must share in the AI technology development achievements to break down the situation of technological hegemony
(二)对外共享人工智能技术发展成果 破除技术霸权状况
As a new technological singularity, generative AI can effectively empower different industries, produce industrial innovation, and greatly improve productivity. It should become a powerful helper for realizing a community with a shared future for mankind. However, most of the value created by AI has not been truly enjoyed by most countries. Instead, it has become a new tool for countries with technological hegemony to expand their monopolistic advantages. At present, the main force in the development of large models is still the leading S&T enterprises, and various R&D entities have not yet reached a consensus on technical standards and usage rules for the development of general large models at the level of international society. At present, China has a certain degree of influence in the development of AI and has the ability to unite other countries to change the “haves” and “have-nots” situation in the field of AI R&D. Therefore, under the new situation, China should continue to adhere to the concept of a community with a shared future for mankind and realize technology and research achievement sharing within the international community so as to slow down the trend of technological polarization on a global scale, win more friends from among developing countries through technology sharing, and breaking the United States’ “Technological Democratic Alliance” (技术民主联盟).
生成式人工智能作为新的科技奇点,能有效赋能不同产业,进行产业革新,大幅提高生产效率,理应成为实现人类命运共同体的有力帮手。但人工智能创造的大多数价值并没有为大多数国家真正享受,反而成为技术霸权国家扩大垄断性优势的新工具。当前,大模型发展的主力军仍是科技龙头企业,各研发主体在国际社会层面上尚且没有达成一致的有关通用大模型发展的技术标准与使用规则。目前,中国在人工智能发展方面具备了一定的影响力,有能力团结其他国家一同改变人工智能研发的“高地”与“低谷”状态。因此,新形势下的中国应继续坚持人类命运共同体理念,在国际社会范围内实现技术和成果共享,以减缓世界范围内的技术两极分化态势,通过技术共享,争取更多的发展中国家朋友,打破美国的“技术民主联盟”。
China should actively explore and discuss international rules and standards related to the development of general large models internationally and actively pursue the right to make rules and technological leadership in new technology fields. This requires China to launch initiatives in multiple areas. In terms of data connectivity, China can take the lead in establishing regional organizations such as a General Large Model R&D Cooperation Organization. On the basis of establishing deeper strategic mutual trust with other countries, China can engage in cooperation based on data and technology exchanges, sign data sharing agreements to build larger databases covering social data from multiple countries, and jointly establish a team of experts from various countries to manage the database. While ensuring data security, this would provide solid support for the training and strengthening of general large model capabilities, effectively broadening the scope of applications and depth of use of the model. In terms of application sharing, China can work with other countries to develop common large-model applications according to local conditions. According to the needs of different countries, such as disaster early warning and social service management, and through methods such as resource exchange and establishment of joint ventures, with guarantees provided by government and technical support and maintenance from leading enterprises, we should cooperate with different countries to develop general large model applications and build digital information hardware facilities, realizing the direct sharing of generative AI achievements. In terms of sustainable development, China can help other countries train the information talents they need and build a basic information talent cultivation system by dispatching scientific research teams, remote guidance, and mutual visits for learning. These practices can not only effectively share AI development achievements and “realize the dreams” of other countries’ informatization and intelligentization development goals, but also effectively enhance China’s influence in international digital information standards and application development paths. In addition, by setting agendas and discussing data processing standards at AI conferences and in international organizations, China can regulate the application scenarios and capabilities of general large models, coordinate the steps taken by various countries in global AI governance, and make positive contributions to guide the development of general large models so that they work for the good.
中国应在国际上积极探索与商讨有关通用大模型发展的国际规则和标准,主动追求新技术领域中的规则制定权与技术主导权,这就要求中国开展多方面行动。在数据联通方面,中国可牵头建立通用大模型研发合作组织等区域组织,在与他国建立更深度战略互信的基础上,围绕数据与技术交换和交流展开合作,通过签署数据共享协议以构建更庞大、覆盖多国社会数据的数据库,由各国共同成立专家团队管理数据库,在保证数据安全的同时为通用大模型能力的训练和强化提供坚实支撑,有效拓宽模型应用的适用范围和使用深度。在应用共享方面,中国可与各国因地制宜的开发通用大模型应用,针对不同国家使用需求,如灾难预警、社会服务管理等方面,通过资源交换、成立合资企业等方式,由政府担保、龙头企业提供技术支撑和维护,与不同国家合作开发通用大模型应用和建设数字信息硬件设施,实现生成式人工智能成果的直接共享。在持续性发展方面,中国可通过派遣科研团队、远程指导和互访学习等方式帮助他国训练所需信息人才,搭建基础信息人才培育体系。这些做法不仅能有效共享人工智能发展成果,“圆梦”他国的信息化智能化发展目标,更能有效提升中国在国际数字信息标准、应用开发路径等方面的影响力。此外,中国可通过在人工智能会议与国际组织中进行议程设定和讨论数据处理标准等方式,规制通用大模型的应用场景与能力,统筹协调各国在全球人工智能治理方面的脚步,为引导通用大模型向好向善发展作出积极贡献。
(iii) We must innovate existing domestic governance tools and improve laws, regulations, and policies in the AI field
(三)创新现有国内治理工具 完善人工智能领域法律法规政策
Network technology is neutral in itself. We must not only observe the impact of emerging technologies, represented by ChatGPT, on the current international security order, but also realize that this is an important opportunity to innovate security governance tools. After all, the new security issues brought about by new network technologies should also be addressed through the development of corresponding governance tools. With the rapid improvement of generative AI capabilities, existing security detection and processing tools are unable to deal with the threats it brings. For example, in the face of forged video and simulated data attacks, traditional information detection tools have difficulty determining the authenticity of information. Only supervision tools built on the same technical foundation can detect and manage such attacks. This also requires enterprises to assume the responsibility of using AI information review technology to regulate the proliferation of false information and frequent criminal frauds that may be induced by AI.
网络技术本身具有中立性,我们不仅要看到以ChatGPT为代表兴起的新兴技术对当前国际安全秩序的冲击,也要意识到这是创新安全治理工具的重要契机,新型网络技术带来的新安全问题也应通过开发相应治理工具予以应对。随着生成式人工智能能力的快速提高,既有安全检测与处理工具难以处理其带来的威胁。例如,面对伪造视频和仿真化的数据攻击,传统信息检测工具难以识别真伪,只有遵循相同技术基底的监管工具才能做出检测与管理。这也要求企业承担起以人工智能信息审核技术规制人工智能可能诱发的虚假信息泛滥和犯罪诈骗频现的责任。
At the same time, generative AI can revolutionize existing governance tools. Based on this technology, enterprises and governments can jointly develop highly automated tools that require data collection and processing, such as natural disaster early warning tools. This can improve society’s early warning and response capabilities for traditional governance issues. Generative AI can also play a supporting role in social services and other fields. Therefore, the comprehensive utilization and development of “generative AI + X” services will help promote the establishment of smart governments and friendly societies. This is a key step in creating an interconnected and intelligent society.
同时,生成式人工智能能够革新既有治理工具。基于该技术,企业和政府能够联合开发自然灾难预警工具等需要数据收集和处理的高度自动化工具,提高社会对传统治理问题的预警和应对处理能力。生成式人工智能也在社会服务等领域发挥辅助作用。因此,综合运用和开发“生成式人工智能+X”类服务将有助于推动智慧政府和友好社会的建立,这是打造万物互联、智能社会的关键一步。
In addition, legal and regulatory systems should also be improved to regulate the development and application paths of generative AI. First, the law should establish a reasonable system of legal regulations around the copyright of the content generated by generative AI and the legitimacy of the source of the content, provide basic legal support for the content created by generative AI, avoid hindering the training and development of generative AI due to violations of intellectual property protection and other regulations so as to encourage and regulate the large-scale production of S&T companies and the deployment of their applications in multiple fields, achieving the stable implementation of the achievements of generative AI research. The abuse of big data by S&T companies itself touches on the right to keep personal information private and the right to know, but excessive restrictions will hinder the development and training of big data models by S&T companies. Therefore, laws and regulations must be introduced to clearly define the boundaries of data that can be used for general large model training and find a balance between ensuring model training and protecting information privacy. For example, using document-based generative AI as an example, the government should negotiate with enterprises on the data types and scale of training texts and “feed” the corresponding content to the AI to avoid intrusion into some unauthorized and private data.
此外,还应当完善法律法规体系,规制生成式人工智能发展与应用路径。首先,法律应围绕生成式人工智能生成内容的著作权、内容来源的正当性建立合理的法律规章体系,为生成式人工智能创造内容提供基本法律支持,避免因违反知识产权保护等条例使得生成式人工智能的训练与发展受到阻碍,以此鼓励和规制科技企业的规模化生产与多领域应用,实现生成式人工智能成果安稳落地。科技企业对大数据的滥用本身就干涉了个人信息的隐私权和知情权,但过分限制则会阻挠科技企业对大数据模型的研发与训练。因此,必须出台法律法规,对通用大模型训练使用的数据明确界限,在维护模型训练和信息隐私之间找寻平衡。例如,以公文型生成式人工智能为例,政府应与企业就训练文本的数据类型和规模进行磋商,“投喂”给人工智能对应的内容,避免造成对部分未授权和隐私数据的侵入。
Second, the government and enterprises should implement effective supervision of the AI industry with clearly defined responsibilities, and implement AI technology safety standards. Enterprises must establish a standardized production system when training and using generative AI, consult with the government and submit documentation in a timely manner on the training data and related feedback of generative AI, focus on cooperation and development of high-quality training data, and ensure the reliability of generative AI capabilities from the source. The government should set up a review team for AI-generated content to regularly review and inspect the operation and use of generative AI. This can then be used as a basis for the assignment of scores linked to the credit rating and preferential tax treatment of development companies, forcing companies to pay attention to safety standards in the process of developing and training AI and ensuring that generative AI does not incorporate discriminatory and biased values into its output framework during the training process. Enterprises should also create compliance design plans to promote AI innovation and ensure system transparency and explainability.
其次,政府与企业应对人工智能产业实行有效且责任明晰的监管,落实人工智能技术安全标准。企业在训练和使用生成式人工智能时必须建立标准化生产体系,对生成式人工智能的训练数据和相关反馈及时与政府进行协商备案,注重对高质量训练数据的合作与开发,从源头上保证生成式人工智能能力的可靠性。政府应设立人工智能生成内容审查组,定期审核和审查生成式人工智能的运转与使用情况,并以此作为打分基础与开发公司的信用评级及税收优待等相联系,倒逼企业重视开发和训练人工智能过程中的安全标准,确保生成式人工智能在训练过程中不会将歧视性和偏见价值观纳入输出框架中。企业也应创建合规性设计计划,促进人工智能创新并确保系统的透明度和可解释性。
Finally, the law should clarify the entities responsible for generative AI and improve the legal liability system accordingly. Transparency and accountability are critical issues in the development and deployment of generative AI, as they are key to ensuring that the technology is trustworthy and remains fair and secure. If a technology or application lacks an entity that can bear responsibility, criminals who use the technology as a criminal tool can easily escape relevant responsibilities. This actually encourages entities in society to abuse it. Therefore, when formulating future laws, we should pay attention to the sharing of responsibility among the designers, users, and maintainers of generative AI, clarify the rights and responsibilities of different entities in the form of laws and regulations, establish corresponding responsibility tracking mechanisms, unify standards for the division of responsibilities, establish reasonable and reality-based principles of attribution, reasonably allocate responsibility for accidents to people or “actual actors,” and cooperate with network information security departments to jointly combat new types of cybercrimes. At the same time, the law must also put forward higher requirements for the producers and maintainers of generative AI and fundamentally reduce the possibility of generative AI being used to commit crimes.
最后,法律应当明确生成式人工智能的责任主体,并据此完善法律担责体系。透明度和可问责特征是生成式人工智能开发和部署的关键性问题,因为这是确保该技术值得信赖与维持公平和安全的关键。如果一项技术或应用缺少主体承担责任,那么使用该技术作为犯罪工具的犯罪分子极易逃脱相关责任,这实际上是鼓励社会主体对其的滥用。因此,在未来法律制定中应当关注生成式人工智能设计者、使用者和维护者三方的责任分担,以法律法规形式明晰不同主体的权利和责任边界,建立相应的责任追踪机制,统一责任划分标准,确立合理并基于现实情况的归责原则,将事故责任合理分配给人或者“实际行动方”,联合网络信息安全部门共同打击新型网络犯罪。同时,法律也要对生成式人工智能的生产者与维护者提出更高要求,从根源上降低生成式人工智能被用以犯罪的可能性。
Conclusion
结语
We can expect generative AI, as represented by ChatGPT, to change the security situation facing the country, but it will also bring new opportunities for national development. The report to the 20th Party Congress pointed out that we must “promote the development of integrated clusters of strategic emerging industries and build a number of new growth engines such as new-generation information technology, AI, biotechnology, new energy, new materials, high-end equipment, and green environmental protection.” This requires us to look at the impact of this technological breakthrough on the country’s development situation from multiple perspectives and realize that generative AI as represented by ChatGPT will serve as a new-generation “Internet platform”, following on the heels of the Internet to become another tool to deeply connect different development fields and accelerating China’s process of building an intelligent society and information superpower.
以ChatGPT为代表的生成式人工智能可预期改变国家面临的安全态势,但同时也为国家发展带来新的机遇。中共二十大报告指出,“推动战略性新兴产业融合集群发展,构建新一代信息技术、人工智能、生物技术、新能源、新材料、高端装备、绿色环保等一批新的增长引擎”。这要求我们多角度看待该技术突破对国家发展态势的影响,认识到以ChatGPT为代表的生成式人工智能将作为新一代的“互联平台”,成为继互联网之后又一个深度联结不同发展领域的工具,并加速中国建立智联社会、信息强国的进程。
The emergence of ChatGPT is not the endpoint of the development of this type of AI, but one of the “singularities” in AI development and application model research. We need to pay full attention to its ample development potential. As similar AI technologies continue to be injected into the development and architecture of digital applications, the software and devices we use in our daily work will become more intelligentized and humanized, and virtual assistants, virtual doctors, and other such things will develop more comprehensive and more innovative functions. In addition, this will break through some of the physical limitations of existing humans, presenting characteristics such as “round-the-clock service, high-precision operations, and multithreaded work.” We can predict that this will achieve substantial improvement in S&T research and development and social service efficiency. In the future, as training scales increase and algorithms are updated, this type of AI will present more comprehensive and powerful functions, with more access ports and more diversified application fields, and will continue to innovate the existing knowledge transfer networks and means of information acquisition in society. It will essentially become the “external brain” of human beings in the digital age, achieving a leap in productivity.
ChatGPT的出现并不是该类型人工智能发展的终点,而是人工智能发展和应用模式研究的“奇点”之一,我们需要充分关注到其身上的充足发展潜力。随着类似的人工智能技术不断注入数字应用的开发和架构当中,我们日常工作使用的软件和设备将变得更加智能化与拟人化,虚拟助手、虚拟医生等事物将发展出更全面、更具创新性的功能,并将突破现有人类所具有的部分物理局限,呈现出“服务全天候、操纵高精度、工作多线程”等特点,并可预期地实现科学技术研发和社会服务效能的大幅提高。未来,随着训练规模增大与算法更新,此种类型的人工智能将展现出更加全面与强大的功能,接入端口更加丰富,应用领域更加多元,不断革新社会既有知识传递网络和信息获取途径,并从实质上成为数字时代人类的“外接大脑”,实现生产效率的飞跃。
However, the development of generative AI such as ChatGPT also means that AI will pose unprecedented and complex challenges to the national security situation, which requires us to promptly and squarely face up to the role of similar AI and its status in societal development. Only in this way can we prepare for the high-tech competition of the future.
但是,ChatGPT等生成式人工智能的发展也意味着人工智能将对国家安全态势带来前所未见的复杂挑战,这就要求我们必须及时正视类似人工智能的角色和在社会发展中的地位,才能在未来的高科技竞争中有备无患。