I. Introduction
— 引言
With the rapid development of the fourth industrial revolution and the iteration of key technologies, space has become a new focus of international strategic competition. After taking office, U.S. President Trump shifted the focus of security strategy to competition between major powers and increased spending in the space sector, aiming to maintain the United States’ absolute advantage in space and seize the high ground in space competition among powers.1 This will not only intensify international competition and games in the space sector, but will also impact global space security and bring new problems for international and national security governance in the broad sense.
随着第四次产业革命的快速发展和关键技术的更新迭代,太空正成为国际战略竞争的新制高点。美国总统特朗普上台以后,将安全战略重心转向大国竞争,并在太空领域频频加码,旨在保持美国在太空领域的绝对优势,抢占未来大国太空竞争制高点。 这不仅会加剧太空领域的国际竞争与博弈,还将冲击全球太空安全,并给广泛意义上的国际和国家安全治理带来新问题。
In 2015, Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) launched a high-speed space internet project called Starlink, which has become a key step in the implementation of the United States’ strategic planning for space in the new era. As a product of the new technological revolution, the U.S. Starlink project has many advanced technology advantages and a broad application market and commercial space. Its goal is to establish a global satellite internet communication system dominated by U.S. technology, and it will have significant impacts and effects on existing global 5G communication technology and future space-based internet systems. At present, the project has already carried out in-depth cooperation with the U.S. military and frequently launched satellites, aggressively seizing near-Earth orbit space spectrum resources. If the project is successfully implemented, not only will there be a problem of outer space resources being forcefully expropriated by U.S. technology, but it will also have a great impact on the low-orbit satellite internet production chain and other technology industry value chains. Based on these understandings, this paper systematically studies the basic content, specific development, and technological characteristics of the U.S. Starlink project, and attempts to conduct an in-depth analysis of its development prospects and possible impacts from the perspectives of market competition, technology competition, and international and national security.
2015 年,美国太空探索计划公司(SpaceX)推出一项名为星链(Starlink)的太空高速互联网计划,成为新时期美国太空战略计划实施的关键一步。美国星链计划作为新技术革命的产物,拥有多项先进科技优势,存在广阔的应用市场和商业空间。其目的是建立美国技术主导的全球卫星互联网通信系统,并将对现存的全球 5G 通信技术和未来的天基互联网系统产生重大冲击和影响。目前,该计划已经与美国军方进行了深度合作并频繁发射卫星,积极抢占近地轨道空间频谱资源。若该计划成功实施,未来不仅将出现外层空间资源被美国技术强势剥夺的问题,同时更会对低轨卫星互联网产业链和其他技术的产业价值链产生极大影响。基于这些认识,本文拟系统研究美国星链计划的基本内容、具体发展和技术特点,并尝试从市场竞争、技术竞争、国际和国家安全等方面对其发展前景和可能产生的影响进行深入分析。
II. Review of domestic and foreign research on the Starlink project
二 国内外关于星链计划的研究综述
As a leader in cutting-edge space technology in recent years, the Starlink project has received attention and research from the foreign and domestic academic communities. As to the basic content of the Starlink project, Kong Chao et al. maintain that once the project is fully deployed as planned, the total number of satellites put in orbit for the project will be nearly six times the number of satellites currently in orbit and operated by all countries in the world, making it the largest-scale constellation project that humanity has been able to propose so far, and it will pose huge challenges for the future communications and internet industries.2 Zhou Yuzhe, focusing more on the technical perspective, argues that Starlink’s full-coverage space-based communication network will be able to completely overcome the regional limitations of traditional land-based communications.3 Zhang Luona et al. believe that SpaceX’s integration of rocket launch and recovery, satellite manufacturing and operation, and ground station manufacturing and services can maximize the cost savings of the Starlink project, so the constellation has a certain market competitiveness and better market development prospects.4 From the perspective of future prospects, Xing Qiang argues that the Starlink project is essentially a constellation of satellites that can provide 5G-level high-speed internet services worldwide.5
星链计划作为近年来全球太空前沿技术的引领者之一,已得到国内外学界的关注与研究。关于星链计划的基本内容,孔超等人认为,一旦按计划完成全部部署,该项目入轨卫星总数就会是目前全球所有国家在轨运营卫星数的近六倍,成为迄今为止人类能够提出的规模最大的星座项目,会对未来的通信互联网产业形成巨大挑战。 周钰哲偏重从技术角度提出,星链的全覆盖天基通信网特质,可以彻底突破传统陆基通信的区域性限制。 章罗娜等从成本和运营层面分析后认为,SpaceX 公司集火箭发射和回收、卫星制造与运营、地面站制造和服务于一体,可以最大程度地节约星链计划的运营成本,因此该计划星座具有一定市场竞争力与较大的市场发展前景。 邢强则从前景判研的角度提出,星链计划本质就是一个通过卫星组成的星座,可为全球提供 5G 级别的高速互联网服务。
Regarding Starlink’s characteristics, Wu Chao et al. observe that the Starlink constellation is characterized by seamless global coverage, convenient access, low latency, and large capacity. In addition, the Starlink satellites are independently produced by SpaceX, so low-cost mass production can be achieved.6 After a comparative study of technologies, Liu Shuaijun et al. maintain that, unlike the terrestrial internet, which provides services to users through fiber-optic home access, and the mobile internet, which provides services to users through the deployment of base stations, low-orbit constellations like Starlink provide communication services to users mainly through satellites. The deployment of terrestrial optical fiber, base stations, etc. is limited by terrain and cannot form effective full-network coverage. Low-orbit constellations, in contrast, have the advantage of “looking down from high above” and can provide internet services to the entire world.7 Zhao Yan et al. summarize the four main characteristics of the Starlink low-orbit satellite internet as: large scale; use of new technologies such as multiple satellites in a single rocket and rocket recovery; low-orbit satellite communications with low latency for use in special terrains; and huge potential commercial value of satellite internet.8 He Kang notes that, in addition to commercial applications, the Starlink project also has military potential and applications, and allows the connection of high-altitude weapons to a global satellite communications network. More connected data and intelligence will lead to a more flexible and more effective combat model.9
关于星链计划的特点,吴超等指出,星链星座具有全球无缝覆盖、接入方便、时延小、容量大等特点,可以通过地面基站和星间链路的链接来优化系统性能,另外,星链卫星由 SpaceX 公司进行自主生产,可以实现低成本大批量快速生产。刘帅军等通过技术对比研究后认为,与地面互联网通过光纤入户、移动互联网通过布设基站为用户提供服务不同,以星链为代表的低轨星座主要通过卫星为用户提供通信服务,而地面光纤、基站等部署受限于地形地貌限制,无法形成有效的网络全覆盖,相较而言,低轨星座具有“居高临下”优势,可面向全球全域提供互联服务。赵燕等总结了星链低轨卫星互联网具备的四大特点:规模庞大;运用一箭多星和火箭回收新技术;适用于特殊地形的低轨卫星通信延时小;卫星互联网潜在商业价值巨大。何康提出,除了商业方面的运用外,星链计划还有着军事潜力和用途,可将高空武器接入全球卫星通信网络,更多连接数据和情报将会带来更灵活也更有效的作战模式。
With regard to the development prospects and impact of the Starlink project, Wu Chao et al. believe that Starlink does not seek to compete with the traditional terrestrial internet for market share. Its target users and application scenarios tend to be niche markets, and it complements terrestrial telecommunications network services.10 Xiang Ligang points out that the idea of replacing optical fiber or 5G with Starlink is unrealistic, but this does not imply that the development model of low-orbit communication satellites represented by Starlink is without merit. Low-orbit satellites can be combined with terrestrial 5G networks to form a unified whole, serving as a supplement to 5G. The future 6G will integrate underground, terrestrial, water surface, and sky into a network system, forming comprehensive interconnectivity between sky and earth.11 Shen Yongyan argues that the vision of all things interconnected via 5G will inevitably require the combined application of various technologies, and the wireless communication nature and diverse uses of satellite communications make it possible to achieve this vision.12 Wang Yong believes that Starlink is a higher “ceiling” that SpaceX is creating for itself, and SpaceX itself can derive three benefits through this project: launch value, economic return on rocket recovery, and orbital frequency occupation.13
关于星链计划的发展前景和影响,吴超等人认为,星链并不追求与传统地面互联网争夺市场,其目标用户和应用场景偏向于小众市场,给地面电信网络服务带来了补充。项立刚指出,以星链取代光纤或者 5G 的设想并不现实,但这并不意味着以星链为代表的低轨道通信卫星发展模式一无是处;低轨道卫星可以与地面的 5G 网络结合成为一个整体,作为 5G 的一个补充,未来 6G 会把地下、地面、水面与天空整合成一个网络体系,形成天地融合的全方位互联互通。 沈永言提出,5G的万物互联愿景必然要求组合应用各种技术,卫星通信的无线通信本质和用途多样性为实现此愿景提供了可能。 汪勇认为,星链是 SpaceX 为自己创造出来的更高的“天花板”,而 SpaceX 本身通过这个计划能够得到三个方面的好处:发射价值、火箭回收经济回报和占有轨位频率。
Regarding the challenges posed by the Starlink project, scholars have mainly analyzed and considered the competition for frequency and orbit resources, network information security challenges, and space debris. Zhou Yuzhe points out that the Starlink project’s intention to commandeer frequency and orbital resources is obvious, and it intends to maximize its potential benefits from “occupying frequency and orbits” in the space field. Since the International Telecommunication Union’s principle for obtaining orbits and spectrum is “first come, first served,” once Starlink has occupied a large amount of orbital and spectrum resources, and other countries need to avoid the frequency bands and orbital positions that have been applied for to avoid mutual interference, it will objectively compress the room for other countries to explore in space.14 Kong Chao et al. maintain that China currently does not have effective regulatory measures for foreign satellite internet systems, and the internet constellation represented by the Starlink project may pose potential security risks and hidden dangers, while rapid formation of space debris will also threaten spaceflight safety.15 Zhang Xue argue that the Starlink project’s intention is to seize orbital resources, and that it will increase the risk of satellite collisions, pose greater challenges for other countries entering outer space.16 Li Cuilan et al. point out that if all the Starlink satellites are launched and then fall to Earth uncontrolled after they are decommissioned or become inoperable, the result will be a large number of satellites entering near-Earth space in a short period of time. This will pose a threat to the safety of satellites in near-Earth space, and the impact on spacecraft that have been in orbit for a long time will be particularly great.17
关于星链计划带来的挑战,学者们主要就其带来的频率轨道竞争、网络信息安全挑战和太空垃圾等几个方面进行了分析思考。周钰哲指出,星链计划霸占频率轨道资源的意图明显,意在最大化其在太空领域“占频占轨”的潜在利益;由于国际电信联盟对待轨道和频谱获取的原则是“先到先得”,一旦星链占据了大量的轨道和频谱资源,而其他国家需要避开已申请的频段和轨位以避免相互干扰,客观上就会压缩其他国家在太空探索的空间。 孔超等认为,目前中国对于国外卫星互联网系统还不具备有效的监管手段,以星链计划为代表的互联网星座可能带来潜在的安全风险和隐患;太空垃圾的快速形成,也将威胁航天安全。张雪提出,星链计划存在抢占轨道资源的意图,会增加卫星碰撞的风险,给其他国家进入外层空间带来更大的挑战。李翠兰等指出,如果星链卫星全部发射,且退役或失效后采用无控陨落,则会导致短时间内有大量卫星进入近地空间,这会对近地空间卫星安全产生威胁,特别是对长期在轨飞行航天器的影响较大。
In addition to the research of domestic scholars, foreign scholars have also devoted considerable attention and analysis to the Starlink project. In particular, Steven Kosiak of the Center for a New American Security (CNAS) points out that SpaceX’s reuse of the Falcon 9 heavy-lift launch vehicle will greatly reduce the Starlink’s launching cost, making the project stand out, and it also has extremely broad development prospects.18 Jonathan C. McDowell has discussed the current number of satellites in low Earth orbit and pointed out that a constellation of about 12,000 internet satellites would dominate Earth’s lower orbit region under 600 km, posing a huge challenge to future astronomical observation and space activities.19 Christopher D. Johnson suggests that a space-based internet formed by Starlink would be more attractive than terrestrial fiber-optic cables, and that providing broader internet access in rural areas and developing countries is an attractive market. Therefore, the use of a group of small satellites to form a network in space would be commercially attractive and promising. Moreover, the Starlink constellation’s impact on astronomical observations would be immediate, and this issue has received significant attention from the astronomical community.20
除了国内学者的研究外,国外学者对星链计划也有较多关注和分析。其中,美国新美国安全中心(CNAS)的史蒂文·科西亚克(Steven Kosiak)指出,SpaceX公司重复利用“猎鹰 9 号”重型运载火箭,会极大地降低星链的发射成本,使星链计划得以脱颖而出,并且具有极为广阔的发展前景。 乔纳森·麦克道尔(Jonathan C. McDowell)讨论了目前低地球轨道人造卫星的数量,并指出,由大约 12 000 颗互联网卫星组成的星链星座将主宰地球轨道下部 600 千米以下的区域,会对未来的天文观测和航天活动形成巨大的挑战。 克里斯托弗·约翰逊(Christopher D. Johnson)提出,星链组成的太空互联网比地面光缆更具吸引力,同时农村和发展中国家更广泛的互联网接入也是一个有吸引力的市场,因此,利用一群小型卫星从太空组网具有商业吸引力和广阔的前景;同时,星链星座对天文学观测的影响也将是立竿见影的,这一问题正受到天文学界的重点关注。
Viewed overall, most of the existing studies analyze the development and industrial impact of Starlink as a cutting-edge technology from a technical perspective. Few of them analyze the Starlink project and its impact on international and national security from the perspective of international strategy and security.
综合起来看,既有研究大多数从技术层面分析了星链作为一种前沿科技的发展和产业影响,很少从国际战略和安全的角度,研究分析星链计划及其对国际和国家安全的影响。
III. Content and characteristics of the Starlink project
三 星链计划的内容与特点
Starlink is not a purely scientific exploration project without a commercial promotion plan. From the start, it has had the grand vision of building a new generation space internet industry. At the same time, Starlink technology integration itself has also had its own prominent characteristics and first-mover advantages.
星链计划并不是一个无商业推广计划的纯科学探索项目,其从一开始就有着构建新一代太空互联网产业的宏伟愿景。同时,星链技术集成本身也有自身突出的特点与先发优势。
(i) Basic information and development status of the Starlink project
(一) 星链计划的基本情况与发展现状
The Starlink project is a low-orbit internet constellation project proposed by SpaceX CEO Elon Musk in 2015. The project had planned to launch 12,000 satellites in three layers at distances of 340, 550 and 1,150 kilometers from the earth between 2019 and 2027, and finally link all the satellites into a huge satellite constellation.21 The Starlink project claims that it will end the network blockages that exist in the world today, but its essence is a global network that is not subject to ground infrastructure limitations. It is a low-cost, high-bandwidth, low-orbit global internet satellite constellation system that covers the entire world, and has extremely high strategic value.
星链计划是 SpaceX 首席执行官(CEO)埃隆·马斯克(Elon Musk)于 2015年提出的一个低轨互联网星座项目。该项目计划在 2019—2027 年,通过发射 1.2 万颗距地球 340 千米、550 千米和 1 150 千米的三层近地轨道卫星,最终使所有卫星链接成一个巨大的卫星星座。 星链计划宣称要结束当今世界存在的网络封锁,但其本质是一个不受地面基础设施限制的全球网络,是覆盖全球的低成本、高宽带低轨全球互联网卫星星座系统,蕴含着极高的战略价值。
Unlike traditional large satellites, Starlink satellites are deployed in low-Earth orbit, which greatly reduces time lags (“latency”), and can achieve global coverage. At the same time, the large number of satellites and the inclination of about 50° mean that only a small zigzag path needs to be traveled to complete data transmission between satellites using the shortest possible straight-line distance. In fact, a “vacuum optical cable” that can be freely spliced and combined in space is established.
不同于传统的大卫星,星链计划卫星采取近地轨道部署,极大地减少了时间的延迟,且可以实现全球覆盖。同时,星链计划庞大的数量和 50°左右的倾角,意味着卫星之间只需要走很小的“之”字形,即可以最接近直线距离的路线完成数据传输,实际上是建立了一个在太空中可随意拼接组合的“真空光缆”。
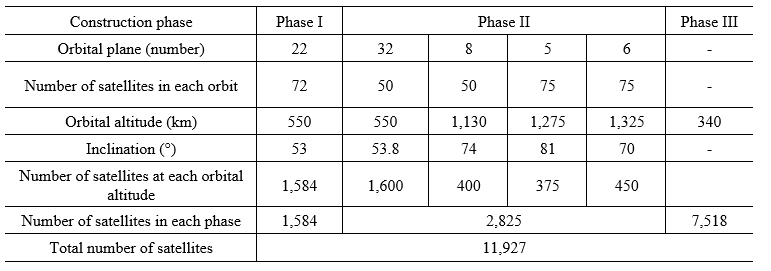
Starlink was originally planned to be completed in three phases. The first phase would deploy about 1,600 satellites in an orbit 550 km above the earth, and by the end of 2020, 800 of those satellites would be used to meet demand for high-speed space-based internet in the United States, Canada, and other parts of North America. The second phase would deploy about 2,800 Ku-band and Ka-band satellites in orbits of 550 km, 1,130 km, 1,275 km, and 1,325 km, to complete the global network; the third phase would deploy about 7,500 V-band satellites in an orbit 340 km above the earth (see Table 1). After the completion of the three-phase plan, the entire globe will be covered.22 Currently, the original plan for the Starlink project’s mega-constellation has been adjusted and orbital altitudes have been reduced. The target orbits are now 550 km, and 30,000 additional satellites have been added, bringing the total to 42,000 satellites.23
星链项目最初计划分三期完成。第一期在距地 550 千米的轨道部署约 1 600 颗卫星,其中在 2020 年底前用 800 颗卫星满足美国、加拿大及北美其他地区的天基高速互联网需求;第二期分别在距地 550 千米、1 130 千米、1 275 千米、1 325 千米的轨道部署约 2 800 颗 Ku 波段和 Ka 波段卫星,完成全球组网;第三期在距地 340 千米的轨道部署约 7 500 颗V 波段卫星(见表 1)。三期计划完成后,就可覆盖全球。 目前,星链计划的巨型星座对最初计划进行了调整并降低了轨道高度,开始以 550 千米轨道为目标轨道,且又追加了 3 万颗卫星,总计达到了 4.2 万颗卫星的规模。
Table 1 Starlink constellation construction plan
表1 星链星座建设计划

 资料来源:作者自制。
资料来源:作者自制。
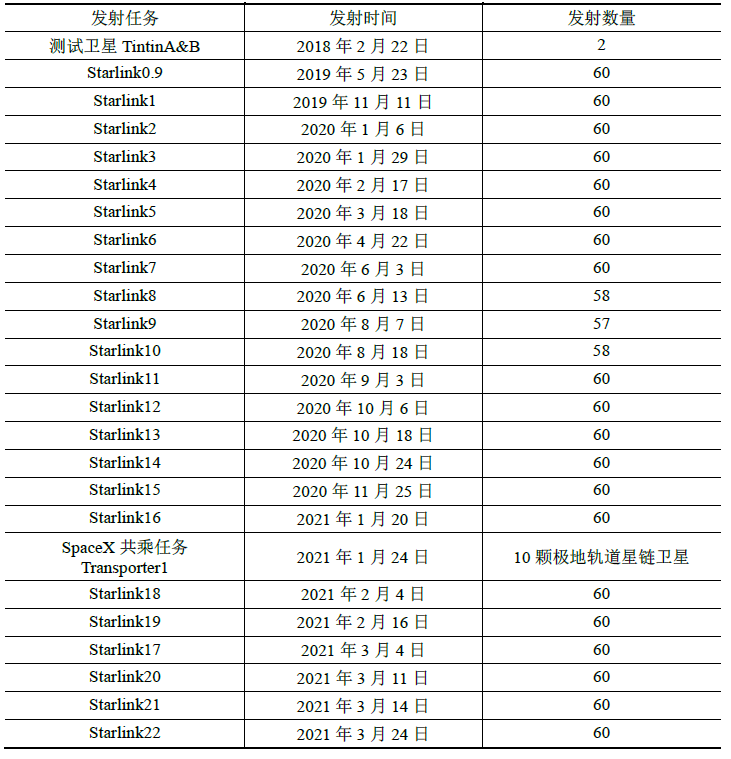
As of March 24, 2021, SpaceX had launched 25 batches of Starlink satellites, totaling 1,385 satellites, of which 1,122 were in orbit. For information on the launch dates and content of each launch, see Table 2.
截至2021 年3 月24 日,SpaceX 已经累计发射25 批次星链,共计1 385 颗卫星,其中在轨操作1 122 颗。关于历次发射时间和内容信息,参见表2。
Table 2 Starlink satellite launch statistics
表2 星链卫星发射统计表



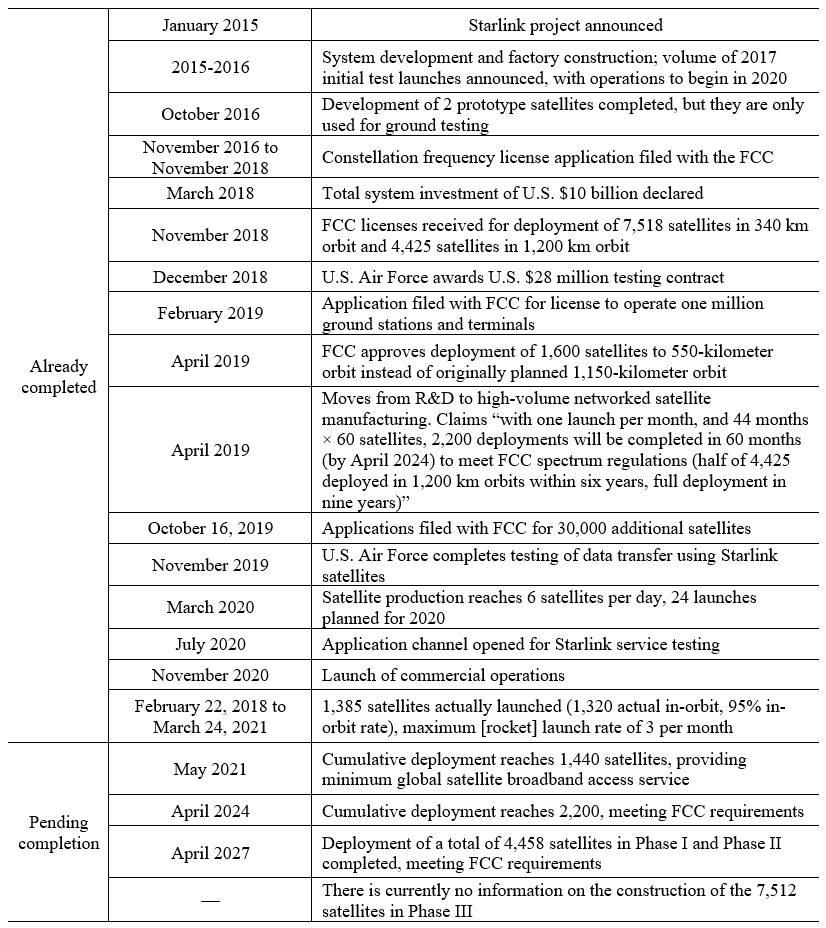
SpaceX has publicly stated that the Starlink network will require 24 launches to achieve widespread coverage, and will be able to cover North America after 14 of those launches.24 Current progress is generally in line with its original plan. Following the 14th successful launch of the Starlink project on October 24, 2020, SpaceX began to provide actual services to Starlink terminal users in November 2020 and launched a public beta program called “Better Than Nothing Beta.” During testing, the estimated speed of Starlink was 50-150 megabytes per second (Mbps), the estimated latency was 20-40 ms. The terminal cost was U.S. $499 (about RMB3,351), and the monthly usage fee was U.S. $99 (about RMB664). This public beta program launch meant that the Starlink project was able to begin serving the public, and became an important milestone in the development of the Starlink project. For the progress of the Starlink project, see Table 3.
SpaceX 公司曾公开表示,星链网络需要 24 次发射来实现广泛覆盖,其中 14次发射后就能覆盖北美地区, 目前的进展情况大体与其原计划一致。2020 年 10月 24 日,星链计划第 14 次发射成功后,SpaceX 在 2020 年 11 月已经开始向星链终端用户提供实际服务,并推出名为“聊胜于无”(Better Than Nothing Beta)的公499 美元(约 3 351 元人民币),每月使用费为 99 美元(约 664 元人民币)。此次公测计划的开展,意味着星链计划开始具备面向公众的服务能力,并成为星链计划发展的重要节点。关于星链计划的推进时间,参见表 3。
Table 3 Timetable of Starlink project progress
表3 星链计划推进时间表

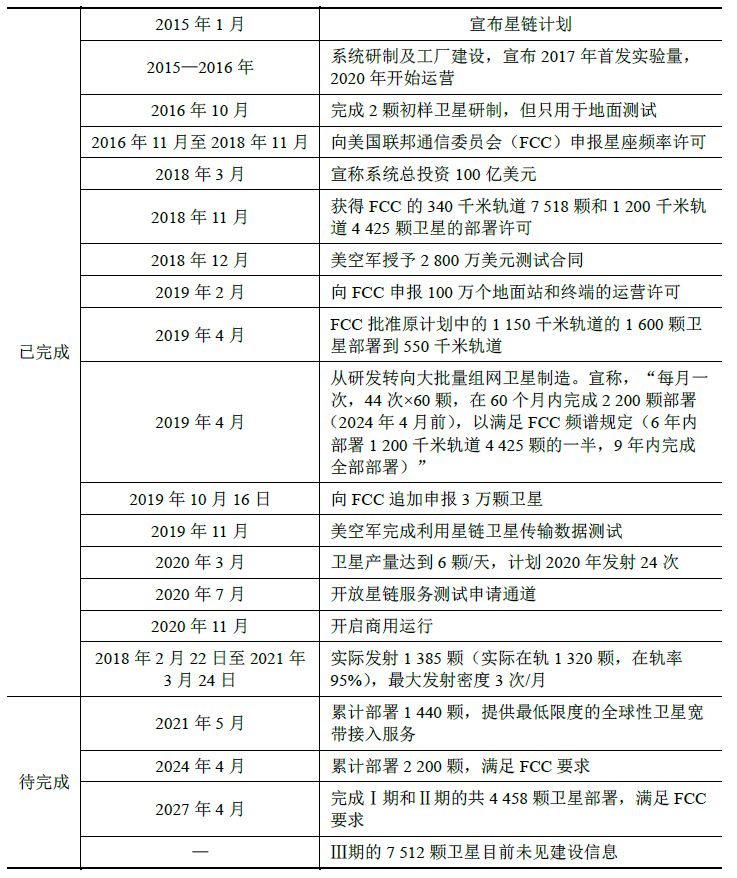

The Starlink system took three years from proposal to test satellite launch, and 15 months from test satellite to a network with the first batch of satellites, with the high-speed networking journey beginning thereafter. Compared to other enterprises that have proposed low-orbit broadband constellations, Starlink can be called the latecomer that got there first. Looking at the changes in the construction plan for the entire network system, there are three obvious trends. First, the number of satellites in the entire system has been increasing progressively, from 4,408 satellites in the first phase (the original plan was 4,425) to 7,518 satellites in the second phase. The third phase, which is currently being applied for, already has as many as 30,000 satellites, and the increasing number of satellites also represents a gradual increase in system capacity. Second, higher and higher frequencies are used. The first phase uses the Ku/Ka band, the second phase uses the V band, and the third phase currently under application uses the E band, in an attempt to use future possible frequencies to position itself strategically against other countries and enterprises. Finally, the satellite orbits are getting lower and lower. The Phase I application was for orbits of 1,100-1,325 km, and in November 2018, orbits of 1,584 satellites were lowered to 550 km; in April 2020, the remaining 2,824 satellites were lowered to orbits of 540-570 km. The second phase again significantly lowered the orbital altitude to 340 km, with the aim of achieving lower transmission latency by continuously lowering the orbit.
星链系统从方案提出到测试卫星发射历经 3 年时间,从测试卫星到首批卫星组网历时 15 个月,此后便开始了高速组网的历程,相较于其他提出低轨宽带星座的企业可谓是后发先至。从整个网络系统建设方案的变化来看,主要有三个明显的趋势。首先,整个系统卫星数量逐步增加,从一期 4 408 颗卫星(原计划 4 425颗)到二期 7 518 颗卫星,目前正在申请的三期已经多达 30 000 颗卫星,卫星数量的增加也代表了系统容量的逐渐提升。其次,使用频率越来越高,一期使用 Ku/Ka 波段,二期使用 V 波段,目前正在申请的三期建设使用 E 波段,企图利用未来可能的频率对其他国家/企业进行战略卡位。最后,卫星轨道越来越低。第一期的申请轨道为 1 100—1 325 千米,2018 年 11 月,将其中 1 584 颗卫星降低至 550 千米;2020 年 4 月,将剩余 2 824 颗卫星轨道降低至 540—570 千米。第二期又大幅降低轨道高度至 340 千米,目的是通过不断降低轨道来获得更低的传输时延。
(ii) Technical characteristics of the Starlink project
(二)星链计划的技术特点
As the world’s largest constellation of low-orbit satellites, the Starlink project has many obvious advantages and characteristics, including an implicit, special strategic value chain.
作为全球业已建成的最大巨型低轨卫星互联网星座,星链计划具有较多明显的优势和特点,包括隐含的特殊战略价值链。
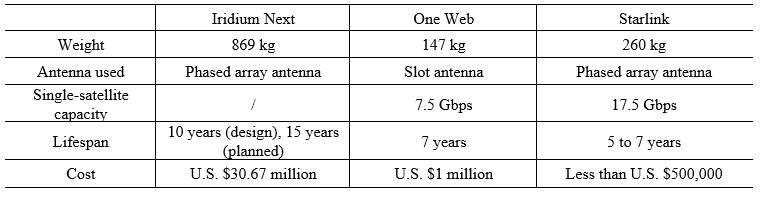
First, the Starlink project’s launch cost is very low. The project’s launch vehicle is SpaceX’s self-developed Falcon 9, which has the world’s most advanced recovery technology, so the rocket can be reused. On August 18 and October 18, 2020, the Starlink-10 and Starlink-13 launches both achieved “one rocket, six launches, six recoveries.” The Starlink-21 launch on March 14, 2021 achieved “one rocket, nine launches, nine recoveries,” just one step away from Musk’s goal of “ten recoveries.” At the same time, SpaceX has been working tirelessly to recover fairings. Since November 11, 2019, SpaceX has made a total of 15 recoveries, recovering a total of 22 fairings, greatly reducing launch costs. Compared to the 1990s when a rocket launch cost tens of millions of dollars, the cost of manufacturing and launching each satellite in the Starlink project is less than U.S. $500,000. Even compared to other low-orbit constellation projects of its own era, the Starlink project is far ahead in terms of cost performance (see Table 4). In addition, SpaceX has been cooperating with other countries and companies through its mature business model of “rockets + satellite deployment + launch services.” The key injector of the Falcon rocket engine is from the U.S. Apollo program, the overall engine design is derived from TRW’s mature products, and the aluminum-lithium alloy and welding technologies used in the rockets are also widely used products. Such a high degree of vertical integration of mature technologies in the upstream, midstream, and downstream of the production chain has greatly reduced the cost of rocket launches.
第一,星链计划的发射成本非常低。该计划的运载火箭是 SpaceX 自行研发的 “猎鹰 9 号”,这一型号的火箭拥有全球最先进的回收技术,可以对火箭进行重复利用。2020 年 8 月 18 日和 10 月 18 日,Starlink10 和Starlink13 的两次发射都实现了 “一箭六飞六回收”。2021 年 3 月 14 日,Starlink21 的发射更是实现了“一箭九飞九回收”,离马斯克期待的“十回收”仅一步之遥。同时,SpaceX 还一直在不懈努力,试图回收整流罩。2019 年 11 月 11 日以来,SpaceX 一共回收了 15 次、共22 片整流罩,大大降低了发射成本。相比 20 世纪 90 年代一次火箭发射动辄需要花费几千万美元,星链计划每颗卫星的制造和发射成本已低于 50 万美元。即使与同时代的其他低轨星座计划比,星链计划的性价比也遥遥领先(参见表 4)。此外, SpaceX 通过“火箭+卫星部署+发射服务”的成熟商业模式不断与其他国家或公司合作。其中,“猎鹰”火箭的发动机关键喷注器来自美国的“阿波罗”计划,发动机整体设计源自 TRW 公司的成熟产品,火箭使用的铝锂合金和焊接技术也是广泛普及型产品。这样一种产业链上中下游成熟技术的高度垂直整合,使火箭发射的成本大大降低。
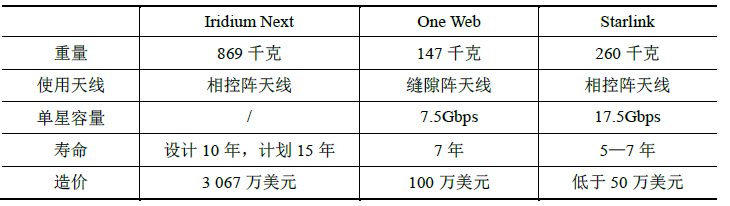
Table 4 Comparison of Iridium Next, One Web, and Starlink satellite parameters
表4 Iridium Next、One Web、Starlink 卫星参数对比


Second, from the theoretical and technical perspectives, the Starlink project can achieve global coverage and fast communication. The modern mobile communication devices currently used rely on electromagnetic waves to transmit signals through mobile communication base stations. Since electromagnetic waves propagate in a straight line, but the earth is an elliptical sphere, as the distance grows, the curvature of the Earth will block the line of sight. The layout of communication base stations is therefore subject to distance constraints, and is limited by topography, so it is impossible to form effective network coverage in remote mountainous areas or at sea. People have solved this problem by building submarine cables and satellite internet. However, electromagnetic waves travel more slowly through submarine cables than in a vacuum. To increase speed, low-orbit satellite internet—the Starlink project—has risen to the occasion. A low-orbit constellation like Starlink has the advantage of “looking down from high above,” and can provide information and communication services globally and to all regions. At present, there are still enormous gaps in the global internet market. As of 2020, nearly half of the world’s population still could not access the internet; by 2025, about 40% of the population will still be unable to access the internet. In addition, weak or nonexistent signals in service scenarios such as aviation, oceans, wilderness, disasters, and wars also provide opportunities for satellite internet to shine.25 From a technical implementation standpoint, the Starlink project offers fast network speed, greatly exceeding traditional fiber optics. According to Elon Musk, the leader of the Starlink project, Starlink provides broadband services of at least 1 Gbps (more than 30 times the current household broadband speed). From July to October 2020, SpaceX completed post-deployment internal testing in North America. The results show that the maximum download speed of the current Starlink is 203.74 Mbps, and the maximum upload speed is 42.58 Mbps. Although these still fall short of Musk’s predicted values, Starlink’s speed has already surpassed 4G, and in theory it will get faster as the number of satellites deployed increases.
第二,从理论和技术的角度看,星链计划可以实现全球覆盖和快速通信。人类目 前使用的现代移动通信设备依赖电磁波,通过移动通信基站进行信号传播。由于电磁波是沿直线传播的,但地球是一个椭圆形的球体,并且随着距离增长,弧形的地球自身便会阻挡视线,通信基站的布置因此就有距离限制,且受限于地形地貌,在偏远山区或海上无法形成有效的网络覆盖。于是人类通过建设海底光缆和卫星互联网来解决这个问题。但电磁波通过海底光缆传输的速度要比在真空中慢,为了提高速度,低轨卫星互联网即星链计划应运而生。以星链为代表的低轨星座具有“居高临下”优势,可面向全球、全域提供信息通信服务。目前,全球互联网市场尚存庞大的空白区域,截至 2020 年,全世界将近一半的人口仍无法上网;到 2025 年,仍会有约 40%的人口无法上网。另外,航空、远洋、野外、灾难和战争等服务场景中的信号薄弱或空缺,也为卫星互联网提供了用武之地。 从技术实现能力看,星链计划提供的网速很快,大大超过传统光纤。根据星链计划主导者马斯克的预测,星链提供的是至少 1Gbps 的宽带服务(这个速度是目前家庭宽带的三十多倍)。2020 年 7—10 月,SpaceX完成了北美地区部署后的内测。结果显示,目前星链的最大下载速率达到 203.74Mbps,最大上传速率为 42.58Mbps。虽然这与马斯克预测的数值仍有差距,但星链的速度已经超越 4G,理论上会随着部署卫星数量的增加而加快。
Third, the Starlink project has great commercial value and broad commercial prospects. Even though Musk has repeatedly stated that the Starlink project will not replace traditional terrestrial telecommunication networks, the project’s market potential and ambitions should not be underestimated. Starlink’s high network speed, low latency, and global coverage will make it extremely competitive in specific business sectors. For example, in the maritime sector, the International Maritime Satellite Organization (INMARSAT), which has a monopoly on civilian maritime communications, can only provide a network speed with a latency of about 600 milliseconds. Once Starlink is commercialized, it will quickly change the global maritime communications landscape. In the global cruise industry, the famous Royal Caribbean International Cruise Line, for example, charges U.S. $10 or U.S. $30 for 60 minutes of internet access, but the high price offers high latency and slow network speeds. With 28.5 million people taking cruises every year, and each person traveling for an average of one week, the Starlink plan’s “cheap, high-speed, low-latency” service will capture the vast international cruise communications market. In addition, the Starlink project will have a huge impact on the global financial investment industry. Due to the limitations of current communication technologies and methods, the prices of commodities traded on the world’s major foreign exchange markets cannot change simultaneously, often resulting in delays of about 100 milliseconds. However, the speed of light in Starlink’s inter-satellite links is faster than that in optical fiber, and delays can be reduced by up to tens of milliseconds. This will be enormously attractive for high-frequency trading programs with trading volumes in the hundreds of millions per second. It is foreseeable that, with the implementation of the Starlink project and the reduction of latency, there will be more commercial application scenarios in the future, and these will bring along considerable commercial value.
第三,星链计划具有巨大的商用价值和广阔的商业前景。尽管马斯克一再表示星链计划不会取代传统的地面电信网络,但该计划的市场潜力和野心不容小觑。星链计划高网速、低时延、全球覆盖的特点,将在特定的商业领域具备超强的竞争力。如在海事领域,垄断了民间海上通信业务的国际海事卫星组织(INMARSAT)目前只能提供延迟为 600 毫秒左右的网速,星链一旦商用,会迅速改变全球海事通信格局;在全球邮轮行业,以著名的皇家加勒比国际邮轮为例,该公司提供的上网服务资费标准为 60 分钟 10 美元或 30 美元一天,高昂的价格换来的却是延迟高、网速慢的服务。以全球每年 2 850 万人次乘坐游轮旅游、平均每人出行一周来计算,星链计划“廉价、高速、低延迟”的服务将占据广阔的国际邮轮通信市场。此外,星链计划对全球金融投资行业也会产生巨大的影响。受制于目前的通信技术和手段,全球各大外汇交易市场的商品交易价格并不能做到同步变动,往往会产生大约 100毫秒的延误,而星链的星间链路光速要高于光纤内的光速,最高可以减少几十毫秒的延误,这对一秒内成交量高达几个亿的高频交易程序而言,将具有极大的诱惑。可以预见,随着星链计划的实施和延时降低,未来还会有更多的商业应用场景出现,并带来可观的商业价值。
Fourth, Starlink has the ability to create international market space and new technology industry value chains. In terms of international market expansion, applications submitted for implementing Starlink’s access services have increased from Canada in North America to Australia and New Zealand in Oceania, as well as the United Kingdom and France in Europe. The Starlink project has already been deployed in many countries around the world. In particular, SpaceX has obtained commercial operation licenses in the United States, Canada, New Zealand, and Australia, and market access applications have been submitted in other countries, including Germany, Spain, Austria, Ireland, Greece, Switzerland, Japan, South Africa, Chile, and Mexico.26 Musk has also said on social media that Starlink services are expected to enter the Indian market in mid-2021.27 In terms of expanding the industrial value chains of new technologies, on October 20, 2020, traditional information technology giant Microsoft announced that its Azure cloud service had formally entered into partnership with the Starlink constellation. This means that Starlink, with its global coverage, will strongly support Azure modular data centers, allowing them to be everywhere, and includes providing cloud computing services for remote areas, with customers including the military, emergency command centers, rescue agencies, and scientific research institutions, thus forming a super-service capability that will allow access to cloud computing from anywhere in the world in the future. Also, according to an analysis by Morgan Stanley, the global aerospace industry could generate more than U.S. $1 trillion in revenue by 2040, compared to U.S. $350 billion today. In this sector, the most important short- and medium-term business opportunities are likely to come from satellite broadband internet access.28 For example, by 2022, half of all commercial flights worldwide will provide internet access, and internet access will be available on all flights by 2035. This will create a new market of approximately U.S. $130 billion.29 Inferring from these kinds of business scenarios, not only will SpaceX’s “multiple satellite, back and forth” rocket launch technology itself be shaped into a unique industrial value chain for the international commercial satellite market, but the accompanying expansion of the business scenario market, including new technology applications such as cloud computing, will also create new industrial value chains in the future.
第四,星链具备国际市场空间与新技术产业价值链的创造能力。在国际市场拓展 方面,目前星链接入服务的落地申请已从北美的加拿大,增加到大洋洲的澳大利亚、新西兰,以及欧洲的英国和法国。星链计划已经在全球多个国家布局,其中,SpaceX在美国、加拿大、新西兰和澳大利亚已经获得了商业运营许可,其他国家包括德国、西班牙、奥地利、爱尔兰、希腊、瑞士、日本、南非、智利和墨西哥等都已经提交了市场准入申请。 马斯克还在社交媒体上表示,星链服务有望在 2021 年中期进入印度市场。 在新技术的产业价值链拓展方面,2020 年 10 月 20 日,传统信息技术(IT)巨头微软宣布该公司旗下的 Azure 云服务与星链星座正式达成合作关系,这意味着全球覆盖的星链将会强有力地支持Azure 模块化数据中心,使其遍布各地,包括为偏远地区提供云计算服务,客户涵盖军方、应急指挥中心、救援机构和科研机构等,从而形成未来全球任何地方都能接入云计算的超强服务能力。另据美国摩根士丹利公司分析估算,到 2040 年,全球航天产业的收入可能超过 10 000 亿美元,而目前这一数字为 3 500 亿美元,其中最重要的短期和中期商业机会则可能来自卫星宽带互联网访问。 以航空网络服务为例,到 2022 年,全球一半的商用航班将提供网络信号;2035 年,网络服务将覆盖全球航班,这将催生约 1 300 亿美元的新市场。 按照这种商业场景推测,不仅是 SpaceX 公司的“一箭多星、来回往返”的火箭发射技术本身将塑造国际卫星商用市场的独特产业价值链,同时其对应的商业场景市场扩展,包括云计算等新技术应用也会打造未来新的产业价值链。
Fifth, the Starlink project has a wide range of military applications and enormous strategic value. Musk has positioned Starlink as a commercial satellite internet project, but its military application prospects are very broad as well. In August 2017, when SpaceX submitted a trademark registration application to the U.S. Patent Office, it expanded the scope of Starlink applications to include satellite communications and transmission, satellite imaging, remote sensing, and other services. If these applications are used in the military, they will further enhance the U.S. military’s combat capabilities, including: communication capabilities and informatization levels; global, all-weather, seamless reconnaissance and surveillance capabilities; space target situational awareness and space-based defense and strike capabilities; non-linear operations; over-the-horizon long-range precision strikes; special operations with unmanned equipment, and other tactical capabilities.30 In addition, the military extension of satellite internet can solve the problem of seamless interconnection between the U.S. territory and overseas military bases, as well as the spectrum occupation and vacating problems in 5G network construction that have long plagued the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD).
第五,星链计划具有广泛的军事用途和巨大的战略价值。尽管马斯克将星链计划定位为商用卫星互联网,但其军事应用前景也十分广阔。2017 年 8 月,SpaceX公司向美国专利局提交商标注册申请时,将星链的应用范围拓宽到了卫星通信与传输、卫星成像、遥感等服务。若这些应用于军事领域,将进一步增强美军的作战能力,包括通信能力与信息化水平,在全球范围内全地域、全天时、无缝隙侦察监视能力,空间目标态势感知能力及天基防御、打击能力,非线性作战、超视距远程精确打击、无人设备特种作战等战术执行能力。 此外,卫星互联网的军事推广可以解决目前美国本土与海外军事基地的无缝互联问题,以及困扰美国国防部许久的 5G 网络建设中的既有频谱占用和腾退问题。
From the standpoint of cooperation between Starlink and the U.S. military, in March 2019, the U.S. Air Force’s Strategic Development Planning and Experimentation Office signed a U.S. $28 million contract with SpaceX requiring the company to conduct military service demonstration and verification using the Starlink constellation within three years. In November 2019, the U.S. Air Force awarded SpaceX a contract called the Defense Experimentation Using Commercial Space Internet (DEUCSI), which aims to explore the use of commercial low-orbit communication satellite constellations to build a globally resilient, highly available, high-bandwidth, low-latency communication infrastructure for the U.S. Air Force in space to support various Air Force combat operations.31 The U.S. military hopes that military users of emerging communication services can sign contracts with commercial satellite companies to conduct testing before a satellite constellation is launched, rather than waiting until the constellation has full network communication capabilities to initiate cooperation.32 In May 2020, the U.S. Army signed a three-year Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with SpaceX to test the feasibility of connecting the broadband network provided by Starlink’s low-orbit internet constellation to the military communication network, so as to help the Army decide whether to purchase Starlink constellation services. Through this cooperation, the U.S. Army will explore issues such as the ground equipment required to use the Starlink broadband network, the amount of system integration work, the cost of equipping soldiers with new satellite communication terminals, whether information transmission is safe and reliable, and so on. The expected goal of the project is to integrate the Starlink broadband network into the existing military systems of the U.S. military.33
从星链与美国军方合作的角度看,2019 年 3 月,美国空军战略发展规划和实验办公室与 SpaceX 签订了价值 2 800 万美元的合同,要求其在三年内利用星链星座开展军事服务演示验证。2019 年 11 月,空军又向 SpaceX 公司授予了一项名为 “商业太空互联网国防实验”(DEUCSI)的合同,旨在探索利用商用低轨通信卫星星座,为美国空军在太空构建全球范围高弹性、高可用性、高带宽、低延时的通信设施,支持空军的各项作战行动。 美国军方希望新兴通信业务的军方用户,在卫星星座发射前期就可以和商业卫星公司签约进行测试,而不用等到这些星座具有全网通信能力才启动合作。 2020 年 5 月,美国陆军与 SpaceX 公司签订了为期 3年的“合作研究与开发协议”(CRADA),以测试星链低轨互联网星座提供的宽带网与军事通信网络连接的可行性,帮助陆军决定是否购买星链星座服务。美国陆军将通过该合作探索以下问题:使用星链星座宽带网需要的地面设备、系统集成工作量,为士兵配置新卫星通信终端的成本,信息传输是否安全可靠,等等。项目预期目标是将星链星座宽带网整合到美军现有的军事系统中。
IV. The U.S. space strategy behind the Starlink project and its impact on international security
四 星链计划背后的美国太空战略及对国际安全的影响
Since its launch, the Starlink project has gradually taken shape as a prototype of space-based internet. The Starlink constellation’s high speed, low latency, and global all-region coverage make it extremely competitive in specific commercial sectors. At the same time, the project’s implementation process and its close cooperation with the U.S. government and military also show that the rapid rise of Starlink is due to the United States’ mature space military-civil fusion system. It reflects the transformation of U.S. space strategy, and will pose huge challenges for international security in the future.
星链计划自推出以来,已经逐步显示出天基互联网的雏形。星链星座互联网高速、低时延、全球、全域覆盖的特点,使其在特定的商业领域已经具备极强的竞争力。同时,该计划在实施过程中与美国政府和军方的深度合作也表明,星链的快速崛起得益于美国成熟的太空军民融合体系,反映了美国太空战略的转型,未来将对国际安全形成巨大挑战。
(i) The emergence of Starlink: A mature U.S. space military-civil fusion system
(一)星链的产生——美国成熟的太空军民融合体系
In the 1980s, the United States launched a multi-domain arms race with the Soviet Union through the “Star Wars” program. This increased the economic burden on the Soviet Union, hastening its collapse. Unlike the Soviet Union, which concentrated national resources on developing the aerospace military industry, the United States’ “arms race” strategy was carried out through two-way cooperation between government and enterprises, and it gradually formed the features of the “military-civil fusion” and “military-to-civilian conversion” model. The development of the U.S. space industry has always been led by NASA and participated in by enterprises. In this model, NASA mainly cooperated with a number of giant private enterprises such as Boeing and Lockheed Martin. However, the high prices charged by large U.S. companies and the persistently high launch costs made U.S. space launches subject to much criticism. Two catastrophic space shuttle accidents that occurred during the same period also caused severe challenges for U.S. space industry development in terms of both national policy and public opinion.34 In order to respond to these challenges, NASA attempted to steer more companies toward investing in the space sector, and to develop the space industry through a new public-private partnership model. That is, by changing the rules of public-private partnerships, a new public-private partnership model was created in order to guide companies to invest and participate in the completion of NASA projects and important tasks, at the same time enhancing the competitiveness of the United States in the space sector.35 Under the new model, traditional vested interests such as Boeing and Lockheed Martin have regained their competitiveness, while a number of small private space companies, led by SpaceX, have also been able to enter the space sector.
20 世纪 80 年代,美国通过“星球大战”计划与苏联展开多领域的军备竞赛,加重了苏联的经济负担,加速了苏联的解体。与苏联集国家之力发展航天军事工业不同,美国的“军备竞赛”战略通过政府与企业的双向合作进行,并逐渐形成“军民融合”和“军用转民用”的模式特点。美国太空产业发展一直采用国家航空航天局(NASA)主导、企业参与的模式。在这种模式下,NASA 主要与几家民营企业巨头如波音、洛克希德·马丁等公司进行合作。但美国大型公司的要价高、发射成本居高不下,使美国的航天发射活动饱受非议,而同时期发生的两起灾难性的航天飞机事故,更是让美国航天工业的发展遭遇来自国家政策和民众舆论两方面的严重挑战。 为了应对这些挑战,NASA 试图通过新型公私合营的方式,引导更多企业对太空领域进行投入,发展太空产业,即通过改变公私合营规则,创造一种新的公私合作模式,引导企业投入资金,参与完成 NASA 的项目和重要任务,同时提升美国在太空领域的竞争力。 在新模式下,传统的既得利益者如波音、洛克希德·马丁公司重新获得了竞争力,同时以SpaceX 为首的一批小型民营航天企业也得以进入航天领域。
SpaceX was founded in 2002. Musk’s initial goal was to form a cheap but effective commercial spaceflight model through low-cost transportation to space. However, since aerospace industry technology had long been monopolized by the U.S. military and large enterprises, SpaceX’s path to growth was not easy. In the first few years after its establishment, SpaceX competed fiercely with other small private aerospace companies in the same field. It eventually stood out by relying on its ability to raise funds and actively responding to NASA’s Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) program. In December 2008, SpaceX won 12 rocket launch project contracts from NASA for amounts ranging from U.S. $20,000 to U.S. $1 billion.36 This marked the beginning of its long-term partnership with NASA and expanded its scale. In June 2010 and August 2012, SpaceX received a total of U.S. $4.93 billion in contracts from NASA to collaborate on the development and design of the Dragon spacecraft to send astronauts into space.
2002 年,SpaceX 公司成立,马斯克的起初目标是通过低成本的太空运输方式,形成廉价但有效的商业航天模式。然而,由于航天领域的技术长期被美国军方和大企业垄断,SpaceX 的成长之路并不容易。在成立之初的几年,SpaceX 与同领域的其他小型民营航天企业展开激烈竞争,最终依靠良好的资金募集能力,积极响应 NASA 推出的商业化轨道运输项目(COTS)而得以脱颖而出。2008 年 12 月, SpaceX 获得了 NASA 多达 12 项、金额在 2 万美元至 10 亿美元之间的火箭发射项目合同, 从此开启了与 NASA 的长期合作并扩大了规模。2010 年 6 月和 2012年 8 月,SpaceX 又相继获得了NASA 给予的共计 49.3 亿美元的合同,与 NASA 共同开发设计“龙飞船”(Dragon),将宇航员送至太空。
Since receiving NASA’s financial and technical support, there has been a constant upgrading of the products SpaceX has introduced. In the short space of a few years, the Falcon 9 rocket has been launched over 20 times, carrying more than 20 tons of payload into low-Earth orbit, and the controlled recovery and soft landing of the first stage of the rocket and its reuse has been achieved, greatly reducing launch costs. SpaceX has also undertaken the development and launch of the Dragon spacecraft. On May 30, 2020, a Falcon 9 rocket successfully sent the SpaceX Dragon capsule into orbit, and two U.S. astronauts arrived smoothly at the International Space Station. This was the first time since 2011 that the United States had used a domestically produced rocket and spacecraft to send astronauts to the space station from its own soil. At the same time, it also fulfilled a goal that SpaceX had promised NASA in 2012, and marked the commercialization of manned space transportation in the United States.
在得到 NASA 的资金与技术支持后,SpaceX 公司推出的产品也在不断升级。在短短几年的时间内,“猎鹰9 号”运载火箭在近地轨道的有效载荷达到20 余吨,发射成功 20 余次,并实现了火箭第一级的可控回收软着陆和重复使用,大大降低了发射成本。SpaceX 还承担了“龙飞船”的研发和发射任务。2020 年 5 月 30 日,“猎鹰 9 号”火箭成功将 SpaceX“龙飞船”太空舱送入轨道,两名美国宇航员顺利到达国际空间站。这是自 2011 年以来美国首次使用国产火箭和飞船从本土将宇航员送往空间站,同时也兑现了 SpaceX 2012 年向NASA 所作的目标承诺,标志着美国载人航天运输走向商业化。
After having received support from the U.S. government and military, SpaceX began to actively “pay it back” by participating in cooperative R&D in many areas of the U.S. military. On March 14, 2017, SpaceX beat out several competitors to win a U.S. $96.5 million contract with the U.S. Air Force to launch GPS-III, the next generation of Global Positioning System satellites.37 SpaceX is to provide launch vehicle production, mission integration, and rocket launching, as well as follow-up value assessment and original research work for GPS-III. In early 2018, SpaceX also began testing for the U.S. Air Force’s Global Lightning project using the Starlink system’s first two test satellites to transmit radio waves to a terminal on board a flying C-12 military transport aircraft. The signal transmission rate at that time reached 610 Mbps, which is 102 times the U.S. military’s current minimum transmission rate of 5 Mbps in theaters of operations, and enough to download a movie in one minute. It is reported that this project will continue, with more military aircraft models to be put into testing.38 On October 5, 2020, the DOD’s Space Development Agency (SDA) and SpaceX signed a U.S. $149 million contract that includes construction of four ballistic missile and hypersonic missile detection and tracking satellites. This was the first time SpaceX officially received a satellite production contract from the U.S. military.39
在获得美国政府和军方的扶持后,SpaceX 开始了积极的“反哺”行动,参与了美国军方多个领域的合作研发。2017 年 3 月 14 日,SpaceX 击败其他几个竞争对手,与美国空军签订了一项 9 650 万美元的合同,发射下一代全球定位系统卫星 GPS-Ⅲ。 SpaceX 将为 GPS-Ⅲ提供运载火箭生产、任务整合、火箭发射,以及后续价值评估和独创性研究工作。同时,SpaceX 在 2018 年初就开始为美国空军的 “全球闪电”项目作测试,借助星链系统最初两颗测试卫星,向一架飞行中的美军 C-12 型军用运输机搭载的终端发射电波,当时信号传输速率达每秒 610 兆字节,是目前美军战区每秒 5 兆最低传输速率要求的 102 倍,足以在一分钟内下载一部电影。据称这一项目将继续进行,更多型号的军用飞机将投入测试。 2020 年 10 月5 日,美国国防部航天发展局(SDA)又与 SpaceX 签订价值 1.49 亿美元的合同,包括建造 4 颗弹道导弹和高超音速导弹探测与跟踪卫星。这是 SpaceX 公司首次正式拿到美国军方的卫星生产合同。
Unlike the “military-to-civilian conversion” of the U.S. aerospace industry at the end of the 20th century, SpaceX’s own development model has become a model for U.S. “civilian-to-military conversion.” This is a new model of U.S. “military-civil fusion” that has developed out of technological progress. By means of U.S. military missions, this model uses the innovation capabilities of small and medium-sized U.S. technology enterprises to actively implement technology sharing and R&D cooperation, contracts, and technology guidance, and finally obtains high-quality, low-cost products through the successful development of private enterprises. This new hybrid “military-civil fusion” system is the fundamental reason for the healthy and sustainable development of the U.S. aerospace industry today. SpaceX’s achievement of such huge breakthroughs in a short time is inextricably linked to the creation of a new model of military-civil fusion in the U.S. aerospace industry.
与 20 世纪末美国航天领域的“军转民用”不同的是,SpaceX 本身的发展模式已经成为美国“民转军用”典范,这是美国“军民融合”在技术进步下发展出来的新模式。这种模式通过美国军方任务、合同、技术引导,利用美国中小科技企业的创新能力,积极实行技术共享和研发合作,最后又通过民营企业发展成功后从中获得质量高、成本低的产品。这种新的混合式“军民融合”体制是造就今日美国航天产业走向良性健康持续发展的根本原因。而 SpaceX 在短时间内取得如此巨大的突破,则与美国航天领域的军民融合新模式创建密不可分。
(ii) Behind Starlink: transformation of the United States’ space security strategy
(二)星链的背后——美国太空安全战略的转型
Since the end of the Cold War, space security has been a key concern of the U.S. government.40 Since Trump took office, the United States has taken frequent action in the space sector, attempting to establish space superiority to serve its great power competition strategy. On June 30, 2017, Trump signed an executive order announcing the reactivation of the National Space Council. Subsequently, the DOD released the National Defense Strategy report, which clearly defined space as a “warfighting domain.”41 In October 2017, experts from the Defense Strategy and Assessment Program of the Center for a New American Security (CNAS) recommended that the Trump administration should formulate a new space strategy to address comprehensive issues in space law, space science and exploration, space commerce, and space security, and maintain the United States’ global space leadership and space hegemony.42 On March 23, 2018, the United States released a new version of the National Space Strategy, which proposed the strategic goal of maintaining the United States’ “strength and competitiveness in the space environment.”43 In February 2019, the DOD released the Challenges to Security in Space report, which details China and Russia’s anti-satellite weapons, including electronic warfare systems, directed energy weapons, and kinetic anti-satellite missiles. It maintains that China and Russia are very likely to pursue the use of laser weapons to destroy, weaken, or damage the satellites (and their sensors) of the United States and its allies, and that they “challenge the U.S. position in space” and pose a “threat to freedom of action in space” for the United States and its allies.44 On August 29, 2019, Trump announced the establishment of the U.S. Space Command, and on December 20, the National Defense Authorization Act of 2020 came into effect, marking the official establishment of the U.S. Space Force. On June 17, 2020, the DOD released a new version of the Defense Space Strategy. This was the first outline of U.S. space strategy announced by the DOD since the establishment of the SDA, the independent Space Command, and the Space Force. The strategic outline calls for the United States to comprehensively push forward space militarization, establish comprehensive space superiority, and ensure the leadership position of the United States in space.45 On August 10, 2020, the U.S. Space Command released the U.S. Space Force’s doctrinal publication, Space Power, further clarifying that the mission of the Space Force is to ensure freedom of action in space, shape a safe space environment, and protect the economic security and prosperity of the United States.46 On December 9, 2020, the U.S. government released the National Space Policy, which once again clearly lays out the principles that space operations should follow, as well as U.S. goals in terms of civil space exploration, commercial growth, and national security.47
冷战结束以来,太空安全一直是美国政府关注的重点。 特朗普执政后,美国在太空领域频频出招,企图建立太空优势,服务于其大国竞争战略。2017 年 6 月 30 日,特朗普签署总统令,宣布重启美国国家太空委员会。随后,美国国防部发布《国防战略》报告,将太空明确定义为“作战领域”。 2017 年 10 月,美国新美国安全中心(CNAS)国防战略与评估项目专家建议特朗普政府,应该制定新的太空战略,着力解决太空法律、太空科学探索、太空商业、太空安全等方面的综合性问题,维持美国全球太空领导权和太空霸权。 2018 年 3 月 23 日,美国发布新版《国家太空战略》,提出了“维持美国在太空领域强大竞争力”的战略目标。2019 年 2 月,美国国防部发布了《太空安全面临的挑战》报告,详细介绍了中、俄的反卫星武器,包括电子战系统、定向能武器以及动能反卫星导弹,认为中、俄极可能寻求使用激光武器摧毁、弱化或损伤美国及其盟友的卫星和其传感器,这些都对“美国在太空领域的地位构成了挑战”,并对美国和盟友“太空行动自由产生威胁”。 2019 年8 月29 日,特朗普宣布成立美国太空司令部;12 月 20 日,《2020 年国防授权法案》生效,标志着美国太空军正式成立。2020 年 6 月 17 日,美国国防部发布新版《太空防务战略概要》,这是继组建美国太空发展局和独立的太空司令部、太空军后,国防部公布的首份美国太空战略纲要。该战略纲要要求美国全面推进太空军事化,建立全面的太空优势,确保美国的太空领导地位。 2020 年 8 月 10 日,美国太空司令部发布美国太空军拱顶石出版物《太空力量》,进一步说明了美国太空军的使命是确保太空的行动自由、塑造安全的太空环境和保护美国的经济安全与繁荣。 2020 年 12 月 9 日,美国政府发布《国家太空政策》,再次明确指出了太空行动应遵循的原则,以及美国在民用太空探索、商业增长和国家安全方面的目标等。
At present, the U.S. space security strategy has the following characteristics: (1) The strategic positioning of space has changed from a strategic support domain to a unique domain of operations; (2) the establishment of a resilient space architecture is an attempt to ensure the strategic superiority of the U.S. military in space; and (3), the redundancy and resilience of space systems are to be enhanced, and military capabilities in space strengthened, through the active development of commercial aerospace.
目前,美国太空安全战略有以下几个特点:一是对太空的战略定位从过去的战略支援领域转变为独特的作战领域;二是建立太空弹性架构,企图确保美军在太空的战略优势;三是通过积极发展商业航天来提升太空系统的冗余与韧性,加强太空军事能力。
The Starlink project’s emergence and promotion completely met the requirements of U.S. space security strategy transformation during the Trump administration. First, the Starlink project had already cooperated with the U.S. Air Force, Army, and Space Force on many occasions since its implementation, and its wide-ranging military applications will significantly enhance the U.S. military’s space combat capabilities. Second, as a representative low-orbit satellite constellation, the Starlink project fully complies with the requirements of the DOD’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) for future satellite systems, and will thus greatly increase the United States’ structure for resilience in space.48 Third, the Starlink constellation was designed, and is being built, by a commercial aerospace company, SpaceX. This allows the U.S. military to take full advantage of commercialized innovative technologies and new commercial operating models, thereby accelerating the application of space technology in military fields.
而星链计划的产生与推进,完全契合了特朗普执政时期美国太空安全战略转型的要求。首先,星链计划实施以来,已经与美国空、陆、天军开展了多次合作,其军事用途广泛,将显著提升美军的太空作战能力。其次,星链计划作为低轨卫星星座的代表,完全符合美国国防部高级研究计划局(DARPA)对未来卫星系统的要求,将大大增加美国太空的弹性结构。再次,星链由商业航天公司 SpaceX 设计、打造,可以使美国军方充分利用商业化的创新技术和新的商业运行模式,加快太空技术在军事领域的运用。
In terms of pace of advancement, the Starlink project also has a certain degree of congruity with the transformation of U.S. space security strategy. In August 2017, DARPA first proposed the concept of “Mosaic Warfare,” which aims to use mosaic forces as the main force for confrontation, and focus the center of gravity of operations on the “Orient-Decide” link of the “Observe-Orient-Decide-Act” (OODA) loop. At the same time, SpaceX officially unified two major internet constellation plans into Starlink and applied for trademark registration. Once the 42,000 satellites in the Starlink project are deployed, it will be like a “mosaic” that surrounds the earth in low orbit. Different satellites within the overall constellation carry different payloads for communication, reconnaissance, navigation, and meteorology, as well as attack and defense, and can quickly shape their perception of the situation and deploy flexibly according to mission requirements. Their “mosaic effect” in future wars, including their role in confusing opponents and taking the initiative, will be prominent.49
在推进节奏方面,星链计划与美国太空安全战略转型也有一定的契合度。2017年 8 月,美国国防部高级计划研究局首次提出“马赛克战”概念,旨在以马赛克兵力作为对抗主力,将作战重心聚焦于“观察—判断—决策—行动”(OODA)作战环的“判断—决策”环节。与此同步,SpaceX 将两大互联网星座计划正式统一为星链并申请商标注册,而星链计划中的 4.2 万颗卫星一旦部署完成,就像是在低轨空间部署了一层包围地球的“巨型马赛克”,整个星座中不同卫星搭载通信、侦察、导航、气象,包括攻防等不同载荷,能够根据任务需求快速塑造感知态势、灵敏机动部署,其在未来战争中的“马赛克效应”,包括迷惑对手、占据主动的作用将会凸显。
In reality, the United States’ space security strategy transformation is being implemented through the Starlink project to a certain extent. On March 12, 2019, the DOD established the Space Development Agency (SDA); and on July 1, the SDA released the requirements for its first project, proposing the concept of a “next generation space architecture,” which aims to rapidly develop a multi-functional small satellite constellation utilizing private company resources and industry best practices. In terms of the military needs of the U.S. military’s new generation of space system construction, this project clearly points in the direction of missile defense and space confrontation, marking a huge shift in the U.S. military’s thinking and approach to the development of space equipment systems.50 Barely one year later, in October 2020, the SDA announced that it would award SpaceX a U.S. $149 million contract and L3Harris a U.S. $194 million contract to build four military satellites for the “Tracking Layer Tranche 0” of the United States’ “Next Generation Space System,” which will be used to provide early warning and tracking information for defense against ballistic, cruise, and hypersonic missiles.51
从现实看,美国太空安全战略转型在一定程度上是通过星链计划来实施的。 2019 年 3 月 12 日,美国国防部组建航天发展局;7 月 1 日,航天发展局发布第一份项目需求,提出“下一代太空体系架构”设想,旨在通过利用私营公司的资源以及行业的最佳实践,快速开发一个多功能的小型卫星星座。这个项目将美军新一代太空体系建设的军事需求明确指向导弹防御和太空对抗,标志着美军太空装备体系发展思路与途径的巨大转变。 仅一年后,即 2020 年 10 月,航天发展局宣布,将授予 SpaceX 公司 1.49 亿美元、L3Harris 公司 1.94 亿美元合同,分别为美国“下一代太空体系”中的“跟踪层 0 期”制造 4 颗军用卫星,用于为防御弹道导弹、巡航导弹和高超声导弹,提供预警和跟踪信息。
Therefore, in the Starlink project’s development, there has been close, comprehensive interaction with the U.S. military in multiple fields. At the strategic level, Starlink has become a key step, an important method, and a vehicle for the U.S. to promote the transformation of its space security strategy. It is not just a simple aerospace commercial project, but also has significant strategic and military implications.
因此,星链计划的发展与美军存在全方位、多领域的密切互动,星链已经在战略层面上成为美国推进太空安全战略转型的关键一步、重要方式和载体,其本身已不仅仅是一个简单的航天领域商业计划,背后有着重大的战略和军事意蕴。
(iii) Starlink raises new international security issues
(三)星链催生国际安全新问题
Starlink is the joint product of the technological development of the fourth industrial revolution and the transformation of U.S. space security strategy for the new era, and its application and promotion of will pose huge challenges for the maintenance of international space security in the future.
星链作为第四次产业革命的技术发展与美国新时期太空安全战略转型的共同产物,其应用和推广将对未来的国际太空安全维护形成巨大的挑战。
First, the Starlink project will pose new threats to the national defense and security of other countries. As a low-orbit satellite internet communication system, Starlink can provide global, dead zone-free, informatized military reconnaissance and communication services to support the operational plans of the Army, Navy, and Air Force. With the space battlefield becoming an increasingly important arena of competition between major powers, core satellite internet technology can be used to threaten the strategic security of other countries and gain the upper hand in future wars. On January 3, 2020, the United States used a UAV to take out Iranian Major General Qasem Soleimani. On November 27 of the same year, Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, head of Iran’s nuclear program and its chief nuclear scientist, was assassinated near Tehran. These actions were made possible by the global high-speed communication and space-air coordination capabilities achieved via satellite networks. If the Starlink project is applied on a large scale in the military field in the future, it will further enhance the U.S. military’s satellite communication and unmanned combat capabilities. At the same time, Starlink’s low-orbit satellites are closer to the ground, which will greatly increase the resolution of the optical sensors carried by the satellites, allowing them to take photos with greater precision. Those 40,000-plus satellites will be equivalent to more than 40,000 high-definition cameras perpetually suspended in the sky, which poses a huge threat to the national defense and security of other countries. What is more, Starlink satellite communications may also change how warfare is waged, to a certain extent. Each satellite can transmit the high-definition pictures and videos it takes over a war zone to front-line commanders through Starlink. At the same time, the huge amount of data collected by UAVs over the battlefield will no longer need to be compressed locally, but will be transmitted in raw form directly to a command center on the other side of the earth via Starlink, and then analyzed by supercomputers to extract useful data and analyze the battlefield situation more precisely, enabling commanders in the war zone to make decisions more quickly and accurately. Starlink will further expand the military superiority of the United States, and in the future may pose new threats to the national defense and security of other countries, especially major powers.
第一,星链计划将对其他国家的国防安全构成新威胁。星链作为一种低轨卫星互联网通信系统,可以提供全球无死角的信息化军事侦察和通信服务,全方位支援陆海空军的作战计划。随着太空战场越来越成为大国竞争的主战场,凭借核心的卫星互联网技术就能威胁其他国家的战略安全,掌握未来战争的主导权。 2020 年 1 月 3 日,美国利用无人机定点清除了伊朗少将卡西姆·苏莱曼尼(Qasem Soleimani);同年 11 月 27 日,伊朗核计划负责人、首席核科学家穆赫辛·法赫里扎德(Mohsen Fakhrizadeh)在德黑兰附近遭暗杀。这些行动均离不开通过卫星网络实现的全球高速通信能力和空天协同能力。未来星链计划若大规模应用到军事领域,将进一步增强美军的卫星通信和无人作战能力。同时,星链这种低轨道卫星距地面更近,会大大增加卫星所搭载的光学传感器的分辨率,使其能够以更高的精度拍摄照片,4 万多颗卫星相当于4 万多个永远挂在空中的高清晰度照相机,这对其他国家的国防安全会构成巨大威胁。不仅如此,星链卫星通信还可能在一定程度上引起作战方式的改变。每一颗卫星都可以将其在战区上空拍摄的高清图片和视频通过星链传输给前线指战员。同时,无人机在战场上空搜集的巨量数据再也不用在本地压缩处理,而是直接将原始数据通过星链传输到远在地球另一端的指挥部,再通过超级计算机从中分析出有用的数据,对战场态势作出更精确的分析,使战区指挥官能够更快更准地进行决策。星链计划会进一步扩大美国的军事优势,未来可能对其他国家,特别是大国的国防安全形成新的威胁。
Second, Starlink will pose new challenges to the information sovereignty and information regulation of other countries. For competition between powers, aerospace resource integration has always been a “battlefield of the future.”52 Starlink has expanded the connotations of national information and network security, making the regulation of cyberspace increasingly complex and much more difficult. Starlink has global coverage, low latency, and high-bandwidth communication capabilities. Such a huge network of low-orbit satellites will be a powerful tool for competing for space information dominance. Once Starlink is deployed globally, it will all but control the power to set the rules for global data exchange. In the rapidly developing information age, securing the power to control data is equivalent to dominating the control of information. At the same time, as a U.S.-designed and developed satellite internet communication project, Starlink aims to provide internet access services worldwide, which will inevitably involve many transnational information and data regulation issues, and thereby create new regulatory gaps. According to the “Wireless Regulations” proposed by the International Telecommunication Union, with the exception of satellite broadcasting services, no country can require another country to exclude its territory from coverage by a foreign satellite network. Therefore, any foreign satellite that covers a country is eligible to provide satellite internet services in the country, and its satellite communication links are not subject to regulation by the country being covered.53 Therefore, Starlink, as a U.S. satellite internet service, will pose a huge challenge to the information sovereignty and information regulation of other countries.
第二,星链计划将对其他国家信息主权和信息监管形成新挑战。空天资源融合一直是大国角力的“未来战场”。 星链拓展了国家信息和网络安全的内涵,使网络空间的监管问题日趋复杂,并且难度大幅提高。星链具备全球覆盖、低时延、高带宽的通信能力,这样一个庞大的低轨卫星网络,是参与竞争空天信息主导权的强有力工具。星链一旦在全球完成部署,几乎会掌握全球数据交换的规则制定权。在高速发展的信息时代,掌握了数据控制权就等于控制了信息主导权。与此同时,星链作为美国设计研发的卫星互联网通信计划,旨在为全球提供互联网接入服务,一定会涉及许多跨国性信息和数据监管的问题,由此带来新的监管空白区域。根据国际电信联盟提出的《无线电规则》,除卫星广播业务外,任何国家不能向其他国家提出外国卫星网络不可覆盖本国领土的要求。因此,任何覆盖该国的境外卫星均具有在该国境内开展卫星互联网业务的资格,并且其卫星通信链路不受被覆盖国的监管。 因此,星链作为美国的卫星互联网业务,将会给其他国家信息主权和信息监管带来巨大挑战。
Third, the huge number of launches planned by the Starlink project will intensify competition for spectrum and space orbit resources. Today, global satellite orbits can be divided into high, medium, and low orbits. The main activity range of low-orbit communication satellites is in space at distances of 300-1,200 km above the Earth’s surface. The orbital range of the Starlink project is 340-1,325 km. If it is fully deployed, it will fill the entire low-orbit channel with over 40,000 satellites. This would be greatly detrimental to the resource utilization efficiency of near-Earth orbits. The International Telecommunication Union adopts the “first come, first served” principle for the orbital frequency spectrum, and in principle, since signal interference occurs between similar frequencies, different satellite communication systems cannot use the same frequency. Therefore, as long as the filing for a space orbit has been made successfully, even if the Starlink satellites have not yet been launched, others will not have the right to use the orbit as well, as projects with later filings cannot conflict with previously filed projects. In this way, the low-orbit region will be almost completely covered by Starlink satellites, which means that low-orbit resources will become increasingly scarce. It will become increasingly difficult for similar projects to avoid Starlink orbits, and they will have to incur additional costs. It can be seen that one of the purposes of the Starlink project is to quickly occupy low orbits through the rapid deployment of a large number of satellites, suppressing other countries’ space industry development, and using technological superiority to deny other countries the right to develop the peaceful use of space.
第三,星链计划庞大的发射量将加剧频谱和空间轨道资源方面的竞争。现今的全球卫星轨道可分为高、中、低三个轨道,低轨通信卫星的主要活动区间在距离地表 300—1 200 千米的太空。星链计划的轨道区间为 340—1 325 千米,如果全部完成部署,将在整个低轨通道布满 4 万多颗卫星,这将大大影响近地轨道的资源利用效率。国际电信联盟对于轨道频谱采取的是“先到先得”原则,且相近频率间会产生信号干扰,原则上不同的卫星通信系统不能使用相同频率。因此,只要空间轨道申报成功,即便星链的卫星还未发射,他人也将无权再使用,后申报项目也不能与之前申报项目产生冲突。如此一来,低轨区域里几乎将被星链卫星布满,这意味着低轨轨道资源越来越稀缺,类似的项目想要规避星链轨道将变得越来越难,而且要付出更多的额外成本。由此可见,星链计划的目的之一,是通过大批量的卫星快速发射部署来迅速占领低空轨道,遏制其他国家的太空事业发展,以技术优势剥夺其他国家和平利用太空的发展权。
Fourth, the huge number of satellites in the Starlink project will pose a huge challenge to the peaceful use of space. The Starlink project plans to launch 42,000 satellites. This means that there will be 42,000 more units operating in an already crowded part of space, inevitably creating a large amount of space junk. Moreover, the lifespan of Starlink project satellites is designed to be five to seven years. After completing their mission, avoiding the uncontrollable “disconnection” of failed satellites and ensuring their safe and reliable recovery is also a major problem that SpaceX will need to face in the future. By occupying space in space, the Starlink project risks harming international aerospace safety, and even threatening the safety of human survival on the ground. In this regard, Harvard & Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics scientist Jonathan McDowell, after analyzing data provided by SpaceX and the U.S. government, found that about 3% of the more than 800 Starlink satellites that have been launched have already failed. If the current failure rate does not decrease, Starlink will generate as many as 1,200 dead satellites in the future, so the amount of space debris will be enormous. This will increase the probability of collisions, which in turn will lead to the generation of more debris, directly threatening the safety of spacecraft and adversely affecting human exploration and utilization of space.54 Even more worrying is that the large number of scrapped satellites may cause the Kessler syndrome in space.55 Therefore, once the Starlink project completes its deployments, it will fill the entire low-orbit region with space junk, threatening the survival of other satellites and even adversely affecting mankind’s plans to launch higher-orbit satellites into space. The most serious consequence is that it would directly affect the ability of countries around the world to explore space in the future, completely “locking” mankind on Earth for centuries.
第四,星链计划庞大的卫星数量将给太空的和平利用带来巨大挑战。星链计划发射4.2 万颗卫星,这就意味着在本就拥挤不堪的太空中又多了4.2 万个运行单位,将不可避免地会产生大量的太空垃圾。而且星链的卫星寿命设计为 5—7 年,在完成使命后,如何避免失效的卫星出现控制不住的“失联”、保证安全可靠的回收也是将来 SpaceX 需要面临的一大难题。星链计划存在着占用太空空间、影响国际航空航天安全,甚至威胁人类地面生存安全的风险。对此,哈佛–史密松天体物理中心的科学家乔纳森·麦克道尔(Jonathan McDowell),在对照分析了 SpaceX 和美国政府提供的数据后,发现已经发射上天的 800 多颗星链卫星中,有大约 3%已经失效。如果目前的故障率不下降,那么星链未来将最多能产生 1 200 多颗“死”卫星,太空碎片数量庞大,会增加相互碰撞的概率,并导致产生更多的碎片,直接威胁到航天器的安全,影响人类探索与利用太空的活动。 更令人担忧的是,大量报废卫星可能造成太空的凯斯勒现象。 因此,星链计划一旦完成部署,将会让整个低轨道区域布满太空垃圾,从而威胁其他卫星的生存,甚至影响人类向太空发射更高轨道卫星的计划,其最严重的后果是直接影响到未来世界各国探索太空的能力,把人类彻底“锁死”在地球上几百年。
Fifth, the Starlink project will have a huge impact on the world’s astronomical exploration and observation. Since most of the satellites in the Starlink constellation are being deployed in low-Earth orbit at an altitude of 340 km, and the moon, the closest object to Earth, is at a distance of 363,300–405,493 km, the dense low-orbit Starlink satellites will inevitably become an obstacle to space observation by astronomers and enthusiasts. As early as May 2019, when the first batch of 60 Starlink project satellites were launched, it triggered a global discussion on business ethics. Many astronomers and astronomical observers criticized SpaceX’s Starlink project for unilaterally changing the appearance of the sky, and possibly causing light pollution and space junk in the future. According to the latest data from the United Nations satellite registration website, there are currently about 2,000 artificial satellites in orbit. If the 42,000 satellites of the Starlink project are successfully launched, there will be about a 20-fold increase. Such a large number of satellites will greatly affect exploration and research conducted by the astronomical community, and the secondary hazards this will bring about for natural disaster prevention and meteorological observation will gradually increase.
第五,星链计划会对世界天文探索和天文观测造成极大的影响。由于星链大部分卫星部署在距地 340 千米的近地轨道上,而距离地球最近的卫星——月球也在遥远的 363 300—405 493 千米外,因此,密布的星链低轨卫星将不可避免地成为天文学者和爱好者观测太空的障碍。早在 2019 年 5 月,星链计划的第一批 60 颗卫星发射时,就引发了一场全球关于商业伦理的讨论,众多天文学家和天文观测者批评 SpaceX 的星链计划单方面改变了天空的模样,且未来可能带来光污染、太空垃圾等影响。联合国卫星登记网站的最新数据显示,目前仍在轨的人造卫星有 2 000 颗左右,如果星链计划的 4.2 万颗发射成功,将会整整增加 20 倍左右。如此繁多的卫星将极大地影响天文学界进行探索和研究,由此带来的自然灾害防御、气象观测等次生隐患也会逐渐增多。
V. The impact of the Starlink Project on China’s National Security
五 星链计划对中国国家安全的影响
When General Secretary Xi Jinping presided over the first meeting of the National Security Commission of the CCP on April 15, 2014, he proposed the need to accurately grasp the new characteristics and trends of the changing national security situation, adhere to the overall national security outlook, and embark on a path of national security with Chinese characteristics. General Secretary Xi Jinping first proposed the overall national security outlook at that meeting, and systematically proposed “11 types of security” for the first time.56 Since then, by refining and deepening the security oulook, a national security system has been formed that involves multiple fields, including politics, national territory, the military, the economy, culture, society, science and technology, networks, ecology, resources, the nuclear field, overseas interests, space, the deep oceans, the poles, and biology. Because the Starlink project has advanced technology featuring space-air integration and interconnectivity, and at the same time superimposes the military strategic intentions of the United States, it will pose huge “compound and cross-cutting” economic, technological, network, and military security challenges for China.
2014 年 4 月 15 日,习近平总书记在主持召开中央国家安全委员会第一次会议时提出,要准确把握国家安全形势变化新特点、新趋势,坚持总体国家安全观,走出一条中国特色国家安全道路。在这次会议上,习总书记首次提出总体国家安全观,并首次系统提出“11 种安全”。 此后,通过对安全概念的完善和深化,形成了涉及政治、国土、军事、经济、文化、社会、科技、网络、生态、资源、核、海外利益、太空、深海、极地、生物等多个领域的国家安全体系。由于星链计划具备空天一体、互联互通的先进技术特点,同时又叠加美国的军事战略意图,其将从经济、技术、网络、军事等方面对中国构成巨大的“复合型、交叉型”安全挑战。
(i) The Starlink project poses serious challenges to China’s satellite internet industry development
(一)星链计划使中国卫星互联网产业发展面临严峻挑战
In April 2020, satellite internet was included in China’s “new infrastructure” for the first time, officially becoming a national key target of investment and development in the future. At the same time, China’s self-developed “Hongyun” and “Hongyan” constellations are also being actively deployed, with the aim of building a “Skynet constellation” that belongs to China. However, compared with the United States’ mature Starlink constellation, which is about to provide global satellite broadband communication services, China’s satellite internet industry development still lags behind. In September 2019, Morgan Stanley stated in a research report that the estimated market value of Starlink was U.S. $120 billion.57 In June 2020, the company released a research report saying that the total output value of the global space industry would exceed U.S. $1 trillion by 2040.58 Chinese research institutions also estimate that the global satellite internet market alone will exceed U.S. $45 billion by 2030.59
2020 年 4 月,卫星互联网首次被纳入中国“新基建”范围,正式成为国家未来重点投资和发展对象。与此同时,中国自主研发的“虹云”“鸿雁”星座也在积极布局,旨在建设属于中国的“天网星座”。然而,相较于业已成熟、即将提供全球性卫星宽带通信服务的美国星链而言,中国的卫星互联网产业发展尚显滞后。 2019 年 9 月,美国摩根士丹利公司在研究报告中称星链公司市场价值估算为 1 200亿美元, 该公司 2020 年 6 月又发布研究报告称,到 2040 年全球太空产业总产值将超过 10 000 亿美元。 中国国内研究机构也估算,到 2030 年,仅全球卫星互联网市场规模可超 450 亿美元。
Morgan Stanley also made a rough forecast of Starlink’s revenue, maintaining that by 2030, Starlink’s market share will reach 33.3%, and its revenue will reach U.S. $15.142 billion. Starlink will thus have a considerable share of the future satellite internet market. In addition, relying on its first-mover advantage, Starlink will be deeply integrated with other fields such the Internet of Vehicles, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud data, and smart city construction. It will comprehensively drive the simultaneous development of upstream and downstream industry production chains, including satellite manufacturing, satellite launching, supporting application, and services, leveraging new economic growth drivers to form a huge Starlink production chain and technology ecosystem. If by that time traditional space powers such as China are not able to make comprehensive breakthroughs in satellite manufacturing scale, launch and recovery costs, and improvement of the supporting production chains, especially in terms of user scale expansion, then due to technology ecosystem constraints unique to internet technology, it will pose a huge challenge to the development of other global satellite internet industry systems, including China’s. This scenario has been fully verified by the two major ecosystems of Apple iOS and Google Android, which have suppressed other technology ecosystems, and it has also been the focus of attention on the part of researchers.60
摩根士丹利公司也对星链的营收作了粗略测算,认为到 2030 年,星链的市场占有率将达到 33.3%,营收将达到 151.42 亿美元,星链会在未来的卫星互联网市场中占据相当大的份额。此外,星链将依托其先发优势,与车联网、物联网、云数据、智慧城市建设等领域深度结合,并全面带动卫星制造、发射、应用配套和服务等上下游产业链等同步发展,撬动全新的经济增长点,形成庞大的星链产业链和技术生态圈。届时,如果中国等传统航天大国不能在卫星制造规模、发射回收成本、配套产业链完善,特别是用户规模扩张等方面进行全面突破,那么由于互联网技术本身特有的技术生态因素制约,将对包括中国在内的其他全球卫星互联网产业体系发展形成巨大的挑战。这种场景在智能手机苹果 IOS 和谷歌公司安卓两大生态系统压制其他技术生态系统中得到了充分验证,同时也被相关研究者所关注。
(ii) The Starlink project will impact China’s 5G technology security and industrial value chain
(二)星链计划将冲击中国的 5G 技术安全与产业价值链
In recent years, with the gradual promotion and popularization of fifth generation communication technology (5G), technical comparisons between Starlink and 5G have increased, and a host of views such as “Starlink will replace 5G” and “Starlink will complement 5G” have emerged.61 To objectively view the relationship between the Starlink project and 5G, a comparative analysis from more levels is required. Looking at application scenarios, 5G is mainly aimed at high-bandwidth, low-latency application scenarios and industries with higher precision requirements, such as autonomous driving and the industrial internet, making them more intelligentized. From the start, the Starlink project has been aimed at users in regions and scenarios that are still not covered by terrestrial internet communications, such as sparsely populated areas, aircraft, ocean-going vessels, scientific exploration, etc. These account for about 3% of the world’s total population.
近年来,随着第五代通信技术(5G)的逐渐推广与普及,关于星链与 5G 之间的技术对比越来越多,“‘星链’代替 5G 论”“‘星链’补充 5G 论”等观点也层出不穷。 究竟如何客观看待星链计划与 5G 间的关系,需要从更多层面进行比较分析。从应用场景看,5G 主要面向高带宽、低时延应用场景和自动驾驶、工业互联网等更高精度要求的产业,使其更加智能化。而星链计划自一开始就将应用场景面向地面互联网通信尚未覆盖的区域,如地广人稀的地区、航空器、远洋船只、科考探险等场景,这些用户约占全球总人口的 3%左右。
In terms of scope of coverage, 5G is like traditional terrestrial internet communication technology in that it requires the construction of ground base stations for information transmission. However, due to factors such as topography and population distribution, in many regions of the world, building 5G base stations is impossible or unsuitable. At the same time, although 5G emphasizes information interaction and the connection of all things, the connected objects are only concentrated in a limited space range up to 10 kilometers above the ground. 5G coverage is therefore very limited. As a low-orbit satellite internet communication technology, Starlink can achieve global, all-weather coverage by “networking” tens of thousands of satellites launched into near-Earth orbit. In contrast with terrestrial internet communication, Starlink can provide information communication services to all areas of the Earth, offering global, all-region internet access capabilities.
从覆盖范围看,5G 与传统的地面互联网通信技术一样,需要通过建设地面基站来进行信息传输,但由于地形和人口分布等因素,全球许多地区无法或者不适合建设 5G 基站。同时,虽然 5G 强调信息交互、万物可联,但连接对象仅集中在陆地 10 千米高度的有限空间范围内。因此 5G 的覆盖面十分有限。星链计划作为一种低轨卫星互联网通信技术,通过在近地轨道发射数万颗卫星“组网”,可以实现对全球无死角、全天候的覆盖。与地面互联网通信相比,星链可面向全球全域提供信息通信服务,具备全球、全域互联网接入能力。
In terms of bandwidth, the theoretical bandwidth of 5G is between 1 Gbps and 2 Gbps, but in actual applications it gradually slows down as the number of base station users increases. The current actual bandwidth of 5G is 200 Mbps-500 Mbps, and it is expected to reach 1Gbps in the future with the further development of broadband technology. The theoretical bandwidth of the Starlink project is 1 Gbps. Since Starlink began internal testing in July 2020, it has reached a maximum bandwidth of 203.74 Mbps, and a maximum upload rate of 42.58 Mbps. Considering that this is merely the bandwidth achieved after launching 1,000-plus satellites, it is believed that bandwidth will improve greatly after the Starlink project achieves global coverage.
从带宽方面看,5G 的理论带宽达到了 1 Gbps—2Gbps,但在实际应用中会随着基站用户的增多而逐渐减速。目前 5G 的实际带宽为 200Mbps—500Mbps,未来随着宽带技术的进一步发展有望达到 1Gbps。星链计划的理论带宽为 1Gbps,从 2020年 7 月开始内部测试以来,星链的最高带宽达到了 203.74Mbps,最大上传速率为 42.58Mbps。考虑到这仅仅是发射了 1 000 多颗卫星后达到的带宽,那么相信在星链计划实现全球覆盖后,其带宽将会大大提高。
In terms of latency, 5G test latency can reach as low as 1 millisecond, and is about ten times better than 4G technology. In the case of IoT, one of the three main 5G application scenarios, the massive number of connections can help operators penetrate into the vertical industries of the IoT, and the low latency and high reliability of the network can help 5G operators achieve business expansion in the industrial internet. Starlink’s latency is similar to that of 4G. The lowest latency since the start of internal testing in July 2020 has been 18 milliseconds, while the average latency has been 25-35 milliseconds.
从时延方面看,5G 的测试时延可以达到 1 毫秒,比 4G 技术优化了十倍左右。在 5G 的三个主要应用场景中,海量物联网连接可以帮助运营商向物联网的垂直行业进行渗透,低时延和高可靠的网络特性可以帮助 5G 运营商实现产业互联网的业务扩张。而星链的时延则与 4G 水平相近,从 2020 年 7 月开始内部测试以来,其最低时延为 18 毫秒,平均时延为 25—35 毫秒。
Overall, 5G technology has obvious advantages in terms of application scenarios and latency. It has a broad market and a wide range of future application scenarios, and is suitable for deployment in areas with complete cellular network coverage and high population density. In contrast, Starlink’s advantages are mainly its wide coverage and ability to achieve global internet communication without dead zones. Its deployment is suitable for areas with underdeveloped networks, mountainous areas, islands, and for emergency communications. More importantly, the military value stemming from the security of Starlink itself is unmatched by current terrestrial transmission network systems. If Starlink can solve the “post-Shannon decoding” (后香农解码) problem, its development prospects will be even more immeasurable.
综合看,5G 技术在应用场景和时延上拥有明显的优势,其市场广阔,面向的未来应用场景丰富,适合布局在蜂窝网络覆盖完善、人口密度大的地区。而相比之下,星链的优势主要是覆盖范围广,具备实现全球无死角的互联网通信能力,适合布局于网络欠发达地区、山区、海岛和应急通信等场景。更重要的是,星链本身的安全性所带来的军事价值是目前地面传输网络系统所无法比拟的。如果星链能够解决“后香农解码”难题,其发展前景则更不可估量。
Starlink and 5G have the potential to enhance each other and develop together. If Starlink and terrestrial 5G networks are integrated, made complementary, and converge, not only could 5G achieve global coverage, but Starlink’s transmission rate and user experience could also be improved through the hybrid application of 5G networks, thereby forming a high-speed, full-coverage, space-ground-integrated information network. International standards organizations, including the International Telecommunication Union, the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), the European Commission-supported SaT5G consortium, and the C-band Alliance (CBA), have begun to study satellite internet-5G network integration issues, such as integration scenarios, core technologies, and network switching.62
星链与 5G 本身具有相互提升和融合发展的潜力。如果星链与地面 5G 网络集成、互补与融合,不仅可实现 5G 的全球覆盖,还可以通过 5G 网络混合应用提升星链的传输速率和用户体验,从而形成天地一体化的高速全覆盖信息网。目前,国际电信联盟、第三代合作伙伴计划(3GPP)、欧盟委员会支持的 SaT5G 联盟和 C 波段联盟(CBA)等国际标准化组织,都开始研究卫星互联网与 5G 的网络融合问题,如融合场景、核心技术、网络切换等。
However, the integration of 5G and Starlink technology is only theoretically feasible, and from the perspective of real-world technology and market system competition, once Starlink’s transmission latency falls to or approaches the latency of 5G, its huge advantages will become apparent. If Starlink can close the latency gap, it will be able to provide low-latency satellite network infrastructure connectivity services for autonomous vehicles, UAVs, unmanned ships, etc. Communication links could then be achieved in places where ordinary signals are not available, such as mountain roads, expressways, national highways, and rural roads not covered by 5G. At the same time, it can also enhance vehicle navigation capabilities and provide more accurate and reliable location services for airborne and vehicle-mounted positioning terminals. Therefore, in addition to the foreseeable technological integration, the competitive factors involved in 5G and Starlink’s two technological systems and the market space cannot be ignored. Currently, the United States continues to stifle China’s Huawei, suppressing China’s technological superiority in the 5G field and inhibiting the overseas market extension of China’s 5G. Its obvious intention is to make “space internet” development a strategic option for the United States to overtake at the turn and enter the 6G era first. Once the United States has elevated the Starlink project to the status of a national competitive strategy (a status it is likely to have already), then from a higher-level national strategic competition perspective, as Starlink project services are gradually rolled out globally (with Starlink arriving in more and more countries in the near future), it is highly likely that China’s 5G overseas market, represented by Huawei, will be gradually weakened or even completely eliminated. In the future, two parallel independent markets and competing industrial value chains will then be formed, with China using 5G and other countries using Starlink. At such time, the global influence of Chinese technology may be further reduced. The worst outcome of this “technology ecosystem” containment strategy would be for Starlink to make a technological breakthrough on latency at the same time as it expands its global market share and application space, while China’s 5G network and technology perhaps become a “technology island” due to global market space suppression. This would have a major impact on China and the global 5G industry value chain.
然而,5G 与星链的技术融合仅在理论上可行,而从现实的技术和市场体系竞争层面看,一旦星链传输达到或接近 5G 的延时,其巨大优势就会凸显。若星链可以弥 补时延差距,就可以为自动驾驶汽车、无人机、无人船等提供低时延卫星网络基础连接服务,那么在 5G 覆盖不到的山路、高速路、国道、乡路等没有普通信号的地方,也可以实现通信链接。同时,它还可以增强汽车导航能力,为机载、车载定位终端提供更加精准可靠的位置服务。因此,除了可预见的技术融合外,5G 与星链的两种技术体系和市场空间的竞争因素不可忽视。当前,美国持续压制中国的华为公司,打压中国在 5G 领域的科技优势和抑制中国 5G 的海外市场推广。其明显意图是,将发展 “太空互联网”作为美国弯道超车率先进入 6G 时代的战略选项之一。一旦美国将星链计划上升到国家竞争战略地位(很有可能已经处于这个地位),那么从更高的国家战略竞争层面上看,随着星链计划服务逐步向全球推行(近期星链的落地国家越来越多),极有可能一步步地减弱甚至完全剔除以华为公司为代表的中国 5G 海外市场,并在未来形成“中国使用 5G、其他国家使用星链”的两个平行独立市场和相互竞争的产业价值链。届时中国技术的全球影响力可能进一步被削减。这种“技术生态型”遏制性战略的最坏结果,就是星链在技术上突破了时延的同时,扩大了全球市场份额和应用领域空间,而中国的 5G 网络和技术由于全球市场空间被压制而可能成为 “技术孤岛”。这对中国,包括全球的 5G 产业价值链会产生重大的冲击性影响。
(iii) Starlink will pose new threats to China’s network, data, and military security
(三)星链计划将对中国的网络、数据、军事安全产生新威胁
Once Starlink has global communication capabilities, it will become a powerful tool for competing for information dominance. Such a global communication constellation will control information in many fields such as aviation, navigation, and finance, and will have almost sweeping power to set the rules for global data exchange. If Starlink makes use of ground-mobile smart vehicles and personal hand-held smart terminals to engage in back-end big data utilization and analysis, the network security and data security threats would be enhanced through “intelligent means.” In March 2021, Musk announced the imminent launch of a concept phone called “Tesla π,” which is to have Starlink connectivity and mind-phone connection functions, as well as the Marscoin mining system, a built in solar panel charging device, ultrasonic fingerprint sensor, high-speed photography, and binding control of Tesla cars. From a technical perspective, it can be foreseen that once the “Tesla π” smartphone is connected to the low-orbit Starlink and ground-based Tesla smart cars to form multi-medium connectivity, assisted by back-end big data analysis and application, the space-ground integration of high-speed information and data transmission will be technically completed. Cyber and data security risks of in all countries would then increase exponentially.
星链一旦具备全球范围的通信能力,将成为一个争夺信息主导权的强有力工具。这样一个覆盖全球的通信星座,将会掌握航空、航海、金融等多个领域的信息,近乎囊括全球数据交换的规则制定权。如果星链通过地面移动智能汽车和个人手持智能终端进行后台大数据利用与分析,那么其对于网络和数据安全的威胁则更会以 “智能方式”增强。2021 年 3 月,马斯克宣布即将推出名为“Teslaπ”的概念手机,该手机具有与星链连接、 脑机连接的功能,还有 Marscoin 采矿系统,带有太阳能面板充电装置和超声波指纹传感器,以及高速摄影、绑定控制特斯拉汽车等先进技术功能。从技术角度可以预见,一旦“Teslaπ”智能手机与低轨的星链、地面的特斯拉智能汽车形成多介质互联,并辅助以后台大数据分析与应用,在技术上完成天地一体化的高速信息与数据传输,那么在整个网络和数据领域,所有国家的网络与大数据的安全隐患都将呈几何级数增加。
Once applied to the military area, Starlink will be able to greatly expand real-time battlefield perception, information interaction, and command and control capabilities, and completely transform the ground information-based combat mode into an “air-space integrated” combat mode. The lowest-level Starlink satellites are distributed in an orbit 340 kilometers above the earth, and their high-speed transmission and low-latency characteristics can promote rapid connection across all branches of the U.S. military, in all directions, and across all regions. Combined with ground transmission stations in the United States, Starlink satellites can form a space-ground integrated monitoring system, which will greatly enhance the U.S. military’s ability to dynamically perceive global and regional battlefields, and will especially enhance the integrated and coordinated combat capabilities of various weapons systems. At the same time, because low-orbit satellites are not constrained by national borders and have a wide reconnaissance range, they can provide intelligence information such as enemy deployments, battlefield terrain, and weapons and equipment. After communication satellites are combined with reconnaissance information transmitted in real time, operational links such as target detection, command decision-making, and target striking will be joined into a real-time operational chain.63 In addition, the commercial positioning and commercial operation of the Starlink project make it difficult for China to effectively defend and retaliate against its military applications legally.
一旦应用于军事领域,星链可以极大地拓展其战场实时感知、信息交互和指挥控制能力,并将地面信息化作战模式彻底转变为“空天集成”作战模式。星链最低层的卫星分布在距地面 340 千米的轨道上,其高速传输、低时延的特点可以推动美国全军种、全方位、全地域的快速连接。星链卫星与美国本土地面传输站相结合,可以构成天地一体监测体系,将大大增强美军全球和区域战场动态感知能力,特别是各种武器系统的集成协同作战能力。同时由于低轨卫星不受国界限制,侦察范围广,能提供诸如敌军部署、战场地形、武器装备等情报信息。实时传输的侦察信息与通信卫星结合后,将把发现目标、指挥决策、打击目标等作战环节连接成实时化的作战链。 此外,星链计划的商业化定位与商业化运营,使中国难以合法地对其军事应用进行有效防御和反击。
VI. Conclusion
六 结语
Since its proposal in 2015 and its first launch in 2019, U.S.-based SpaceX’s Starlink project has made 15 successful launches to deploy 1,122 satellites into predetermined orbits, making it the world’s largest satellite internet communication constellation. As of the end of October 2020, Starlink had completed full coverage of North America and sent testing invitations and package price quotes to users. At the same time, Starlink is also actively exploring the global market in the hopes of making higher commercial returns. At present, while the international communications industry is more concerned about Starlink’s commercial value and market competition, and tech enthusiasts are keen to discuss the “Iron Man” myth in fields of technology shaped by “space-air technology interconnection,” the complex national and international security issues inherent in the Starlink project itself have not received enough attention.
自 2015 年提出、2019 年首次发射以来,美国 SpaceX 星链计划成功发射 15 批次,部署了 1 122 颗卫星至预定轨道上,并一举发展成为全球最大的卫星互联网通信星座。截至 2020 年 10 月底,星链计划已经完成对北美地区的全覆盖,并向用户发送了测试邀请和套餐报价。与此同时,星链还在积极开拓全球市场,期待获得更高的商业收益。当前,国际通信业界更多关心星链的商业价值和市场竞争,技术爱好者热衷讨论“空天技术互联”塑造的技术领域“钢铁侠”神话,而星链计划本身所隐含的复杂的国家与国际安全问题却没有得到足够的重视。
The Starlink project has the advantages and characteristics of low launch costs, global coverage, fast network speeds, and broad commercial prospects. Between Starlink and advanced 5G technologies, a relationship of mutual substitution and potential competition exists. If the Starlink project further accelerates its deployment and can make a breakthrough in new decoding technology to achieve low latency comparable to 5G technology, it will be sufficiently competitive in commercial markets to directly threaten the application and extension of existing global 5G network technology. At that time, the United States may use a “technology + market” alliance to promote Starlink, and use “national security” and “values” as excuses to exclude 5G technology from China from the global next generation communication network market.64 In that case, China’s 5G technology, in which heavy R&D investment has been made, including 5G patents already owned in other countries, would fail to achieve global “market spillover,” and the probability of its becoming a “technology island” would also greatly increase, which would in turn cause a large amount of sunk global investment costs and damage to the industrial value chain, and create new and complex economic security issues.
星链计划具有发射成本低、可实现全球覆盖、网速快、商业前景广等优势与特点。星链与先行的 5G 技术存在相互替代和潜在竞争的关系。如果星链计划进一步加快部署,并能够突破解码新技术,实现媲美 5G 技术的低延时,那么其在商业市场上将产生足够的竞争力,直接威胁到现有全球 5G 网络技术的应用与推广。届时,美国可能会采用“技术+市场”联盟的手段推广星链,并以“国家安全”和“价值观”为由, 将中国为代表的 5G 技术排斥出全球下一代通信网络市场。果然如此,研发投入巨大的中国 5G 技术,包括他国已经拥有的 5G 专利将不仅无法实现全球 “市场溢出”,而且成为“孤岛技术”的可能性也会大大增加,进而造成大量的全球投资沉没成本和产业价值链损毁,产生新的复杂的经济安全问题。
From a broader perspective of international and national security, the Starlink project is to some extent a product of, and vehicle for, the transformation of U.S. space security strategy. It has far-reaching strategic significance with regard to the United States’ seizure of space resources and orbital frequencies, improvement of the U.S. military’s communication technology and capabilities, and improvement of the United States’ “space-air-ground integrated” combat capabilities, including deployment of its “endless frontier” space strategy. At the same time, Starlink’s large-scale deployment will not only pose new challenges to space security, but its impact on astronomical observation activities and disaster prevention may also be international in nature. The new threats that Starlink’s commercial operations pose to the information security, data security, and military security of other countries are real and unavoidable. In particular, the diversity of intelligent terminals and the interconnection of “space-ground” information and global data exchange, brought about by the integration of new technologies, will create new “compound and cross-cutting” security issues and challenges for the national security and social and economic development of other countries. Therefore, when looking ahead technologically to a “future with a sea of technological stars” that Starlink is itself developing, it is even more necessary to pay attention to, and be vigilant about, the national security games and other deeper issues that lie behind it.
从更广泛的国际和国家安全角度看,星链计划在某种程度上是美国太空安全战略转型的产物和载体,对于美国抢占太空资源与轨道频率,提高美军的通信技术与能力,完善美国“空天地一体”作战能力,包括对美国“无尽边疆”的太空战略部署均有着深远的战略意义。同时,星链的大规模部署不仅对太空安全构成新挑战,其对天文观测活动和灾害防御产生影响也可能是国际性的。星链商业化规模运营对他国信息、数据安全与军事安全造成的新威胁是现实的和不可回避的,特别是其新技术融合带来的多样性智能终端与“天空地”信息互联和全域数据交换,将给他国的国家安全与社会经济发展带来“复合型、交叉型”新安全问题和挑战。因此,当在技术上展望星链本身拓展的“技术星辰大海未来”时,更要重视和警惕其背后所蕴含的国家安全博弈等更深层次的问题。